- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• Gas–liquid mass transfer rule in gas–liquid–solid mini fluidized bed was found.
• Fluidized particles play an important role in enhancing gas–liquid mass transfer.
• Mass transfer trend in gas–liquid–solid mini fluidized bed was reported.
• Mass transfer trend in gas–liquid mini bubble column was reported.
• Mass transfer trend in mini fluidized bed is similar to mini bubble column.
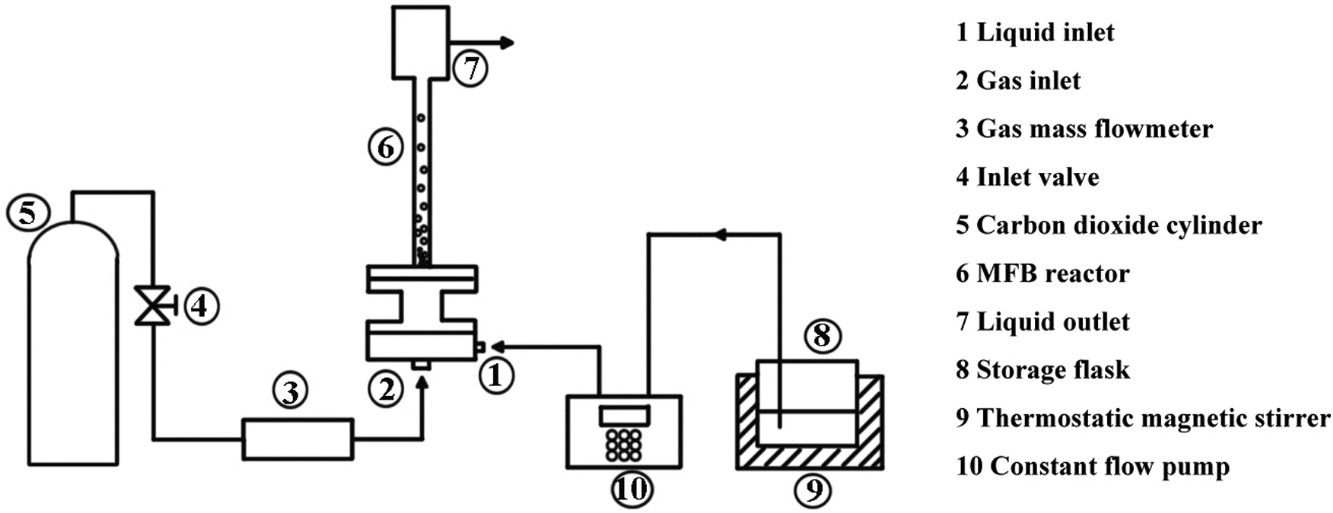
The gas–liquid–solid mini fluidized bed (GLSMFB) combines the advantages of fluidized bed and micro-reactor, and meets the requirements for safety and efficiency of green development of process industry. However, there are few studies on its flow performance and no studies on its mass and heat transfer performance. In this paper, the characteristics of gas–liquid mass transfer in a GLSMFB were studied in order to provide basic guidance for the study of GLSMFB reaction performance and application. Using CO2 absorption by NaOH as the model process, the gas–liquid mass transfer performance of GLSMFB was investigated. The results show that the liquid volumetric mass transfer coefficient and the gas–liquid interfacial area both increase with the increase of the superficial gas velocity within the experimental parameter range under the same given superficial liquid velocity. At the same ratio of superficial gas to liquid velocity, the liquid volumetric mass transfer coefficient increases with the increase of the superficial liquid velocity. Fluidized solid particles strengthen the liquid mass transfer process, and the liquid volumetric mass transfer coefficient is about 13% higher than that of gas–liquid mini bubble column.