- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
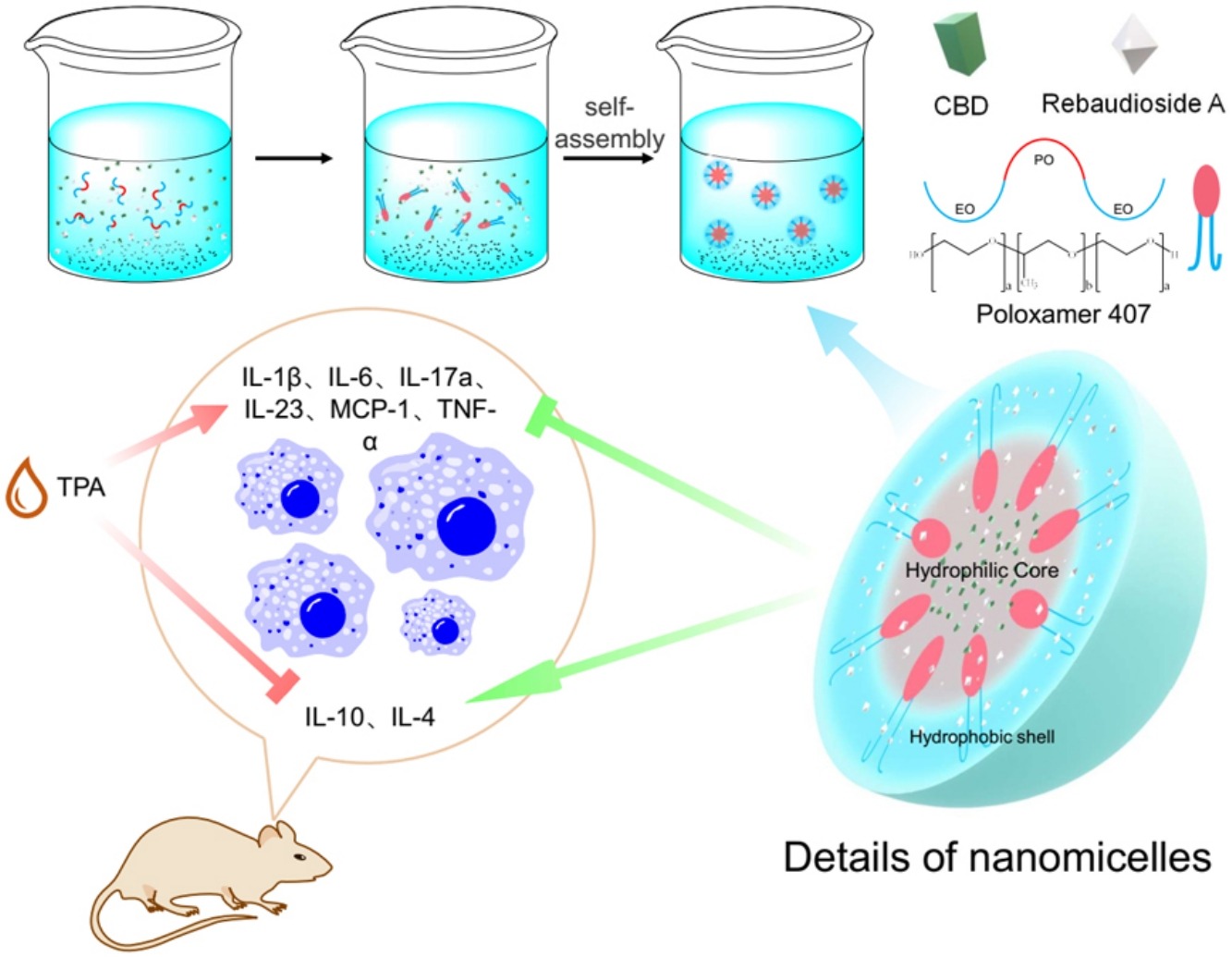
• Cannabidiol (CBD) nanomicelles with a drug loading of 14.29% were prepared using P407.
• Anti-inflammatory effect of CBD nanomicelles was better than that of CBD.
• No obvious evidence indicated toxicity to the liver and kidney.
• Solubility of CBD was improved.
Cannabidiol (CBD) shows great anti-inflammatory potential; however, the hydrophobicity and strong first-pass effect of CBD leads to its extremely low oral bioavailability. Poloxamer 407 (P407) is a triblock copolymer composed of (poly)ethylene oxide (PEO) and (poly)propylene oxide (PPO) sections. It has a PEO-PPO-PEO structure, which is widely used in the preparation of drug delivery systems that are highly biocompatible. When it reaches a certain concentration in water, P407 can self-assemble into a micelle structure containing a hydrophobic core and a hydrophilic shell. A potential approach to enhancing the oral bioavailability of hydrophobic drugs incorporating them into the hydrophilic carrier. We prepared CBD nanomicelles with a drug loading of 14.29% by a cosolvent evaporation method using P407 with appropriate antioxidants. Cell experiments indicated that anti-inflammatory markers (IL-4 and IL-10) increased, while inflammatory markers (TNF-α and IL-6) decreased. Moreover, animal experiments showed that inflammatory cells were inhibited by CBD nanomicelles, and the anti-inflammatory effect of micelles was better than that of CBD, while no obvious evidence indicated toxicity to the liver and kidney.