- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
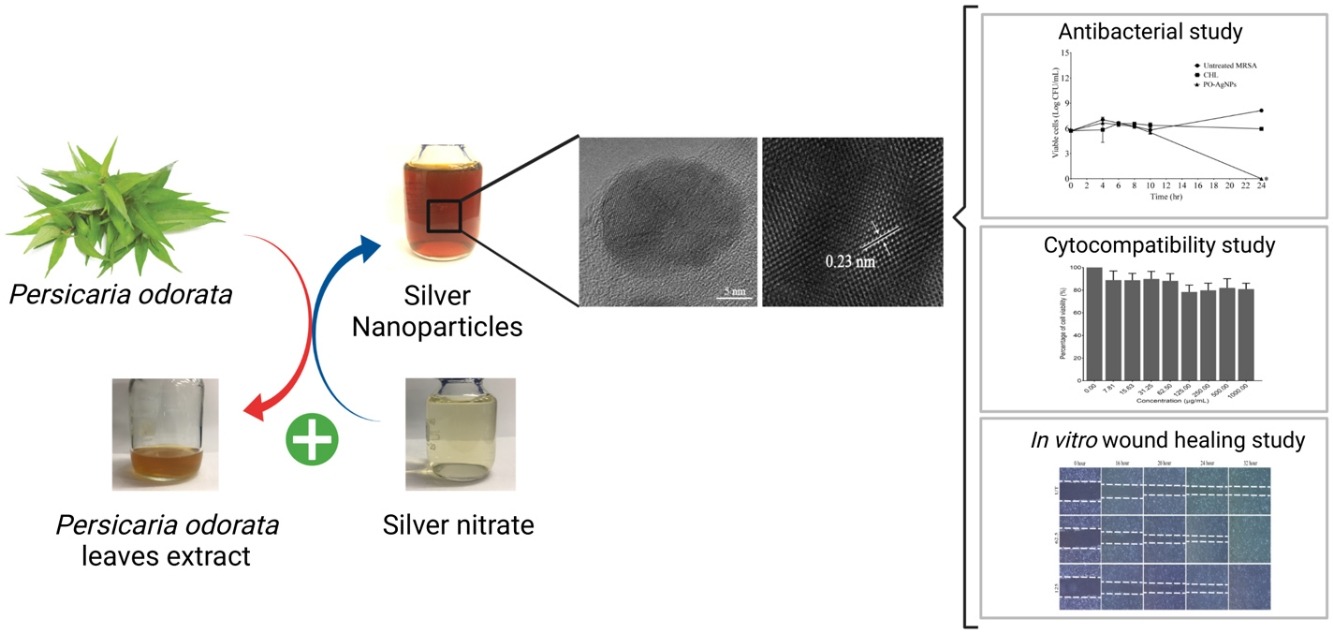
• Biogenic synthesis of PO-AgNPs was mediated by aqueous extract of Persicaria odorata leaves.
• PO-AgNPs showed bactericidal activity against Gram-positive bacteria.
• PO-AgNPs were shown to be non-toxic to HSF 1184 cells.
• PO-AgNPs facilitated wound healing by enhancing cell migration in vitro.
Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles (b-AgNPs) utilising plant extract has gained the interest of researchers due to the environmentally friendly and cost-effective technique. However, the extent of its application in the biomedical field remains scarce. This study evaluates the antibacterial, cytocompatibility, and wound healing activities of synthesised AgNPs using Persicaria odorata leaves extract (PO-AgNPs). The formation of PO-AgNPs was observed by visual colour changes and verified by ultraviolet-visible (UV–vis) spectrophotometer, which revealed a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) at around 440 nm, and further confirmed by X-ray diffraction (XRD). Characterisation using Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy showed biomolecules from the leaves extract presented together on PO-AgNPs. Field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM) and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM) images revealed PO-AgNPs nanospheres with diameters of 11 ± 3 nm. Disc diffusion test (DDT) and minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) analysis resulted in a dose-dependent inhibition of PO-AgNPs against tested Staphylococcus epidermidis and Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). These results were further corroborated by time-kill kinetic assay which revealed that PO-AgNPs were bactericidal against both strains 24 h post-treatment. Cytocompatibility and in vitro wound healing evaluation against normal human fibroblast cells, HSF 1184 inferred that PO-AgNPs are non-toxic to normal cells and able to enhance cell migration as compared to the non-treated cells. Therefore, PO-AgNPs are biocompatible and possess antibacterial and wound healing capabilities that are useful in biomedical applications.