- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
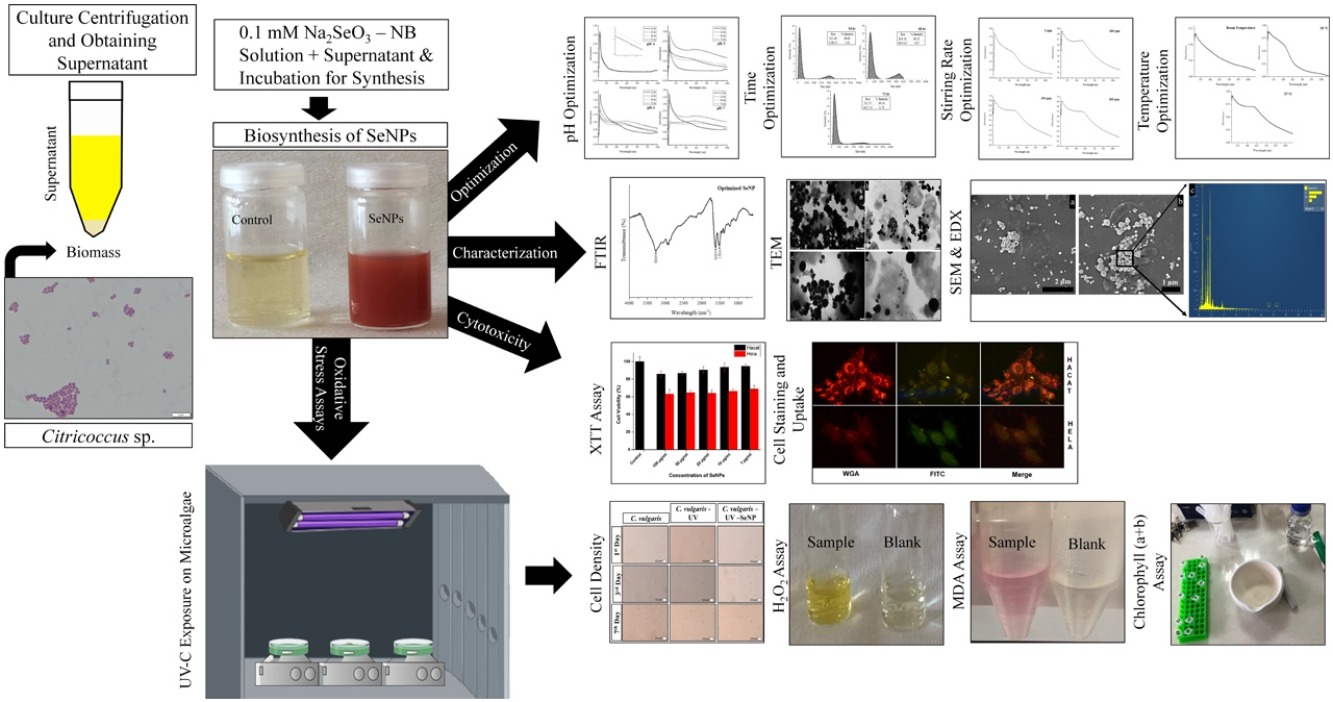
• Selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) were synthesized using supernatant of halophilic bacterium Citricoccus sp..
• Effects of SeNP was investigated on oxidative stress induced by UV in Chlorella vulgaris.
• Changes in H2O2, MDA, chlorophyl (a + b) content and cell density were monitored.
• Synthesized SeNPs alleviated the adverse effects of UV stress in microalgae.
Since nanoparticle synthesis via chemical and physical methods is expensive and includes hazardous chemicals, biosynthesis has emerged as an environmentally friendly, clean and viable alternative. The present study reports the synthesis of selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) using Citricoccus sp.. For the production of SeNPs, the influence of some parameters (time, pH, temperature and stirring rate) was studied. Optimum synthesis conditions were found as pH 8, 24 h reaction time, 37 °C and 150 rpm. Synthesized particles were spherical and were 104.46 ± 50.82 nm with a zeta potential of –20.43 ± 0.41 mV. Afterward, the effects of the nanoparticles on oxidative stress biomarkers, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), malondialdehyde (MDA), chlorophyll (a + b) and growth rate, subsequent to UV-C irradiation on Chlorella vulgaris were investigated. In culture contains nanoparticle and UV-C exposed, the amount of H2O2 and MDA decreased on the 1st, 3rd and 7th days following UV exposure compared to UV-applied group, while optical density and cell density increased, the amount of chlorophyll (a + b) changes were statistically similar. Consequently, it has been shown that the synthesized SeNPs alleviated the adverse effects of UV stress in microalgae.