- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
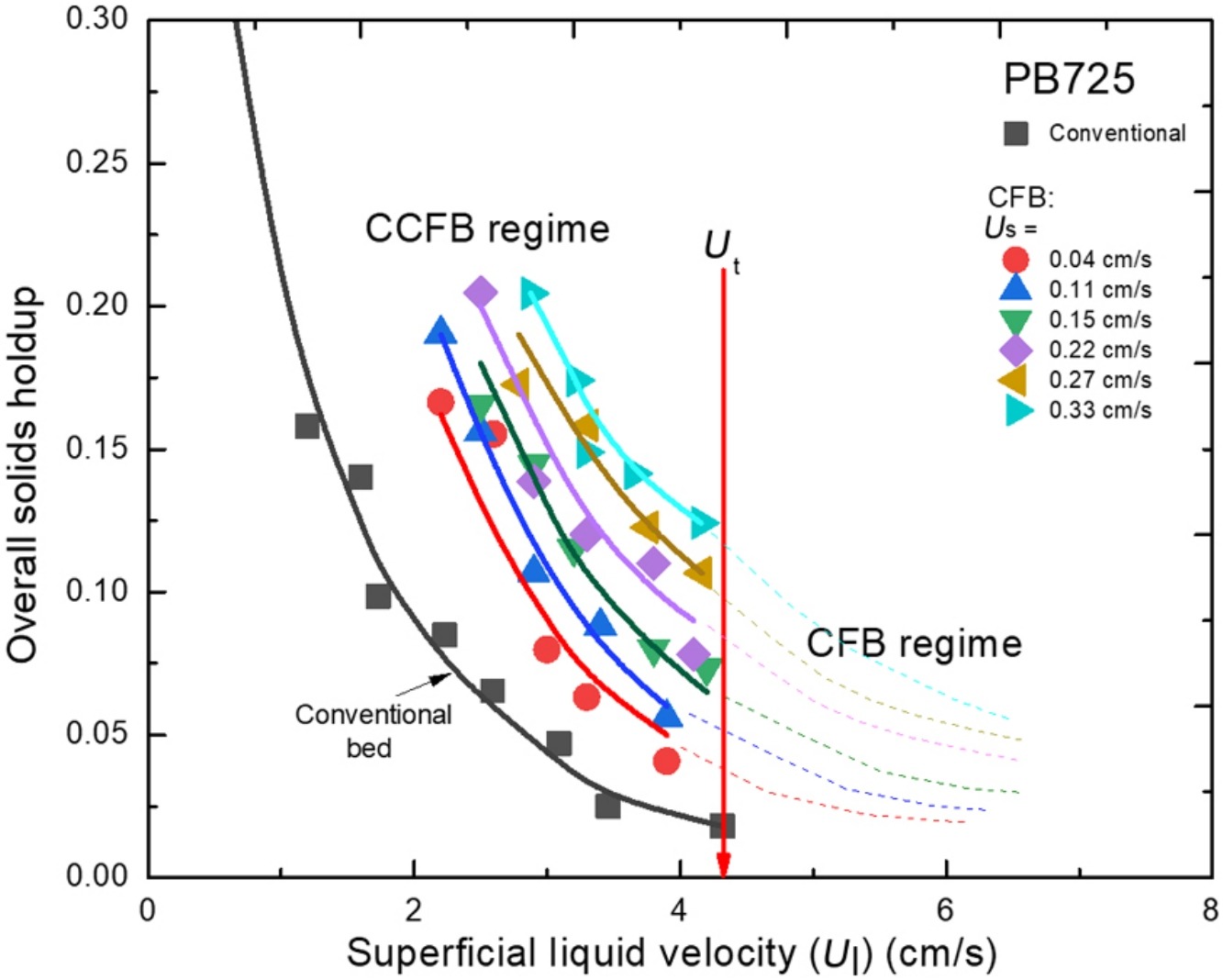
• A newly-proposed liquid–solid circulating conventional fluidized bed (CCFB) was experimentally studied.
• Liquid fluidization with external circulation below particle terminal velocity was realized.
• The axial solids holdup is uniform in a wide range of operating conditions.
• A higher overall solids holdup is achieved in CCFB compared to conventional fluidization.
• Particles with higher terminal velocity have higher average solids holdup in CCFB.
A new type of liquid–solid fluidized bed, named circulating conventional fluidized bed (CCFB) which operates below particle terminal velocity was proposed and experimentally studied. The hydrodynamic behavior was systematically studied in a liquid–solid CCFB of 0.032 m I.D. and 4.5 m in height with five different types of particles. Liquid–solid fluidization with external particle circulation was experimentally realized below the particle terminal velocity. The axial distribution of local solids holdup was obtained and found to be fairly uniform in a wide range of liquid velocities and solids circulation rates. The average solids holdup is found to be significantly increased compared with conventional fluidization at similar conditions. The effect of particle properties and operating conditions on bed behavior was investigated as well. Results show that particles with higher terminal velocity have higher average solids holdup.