- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
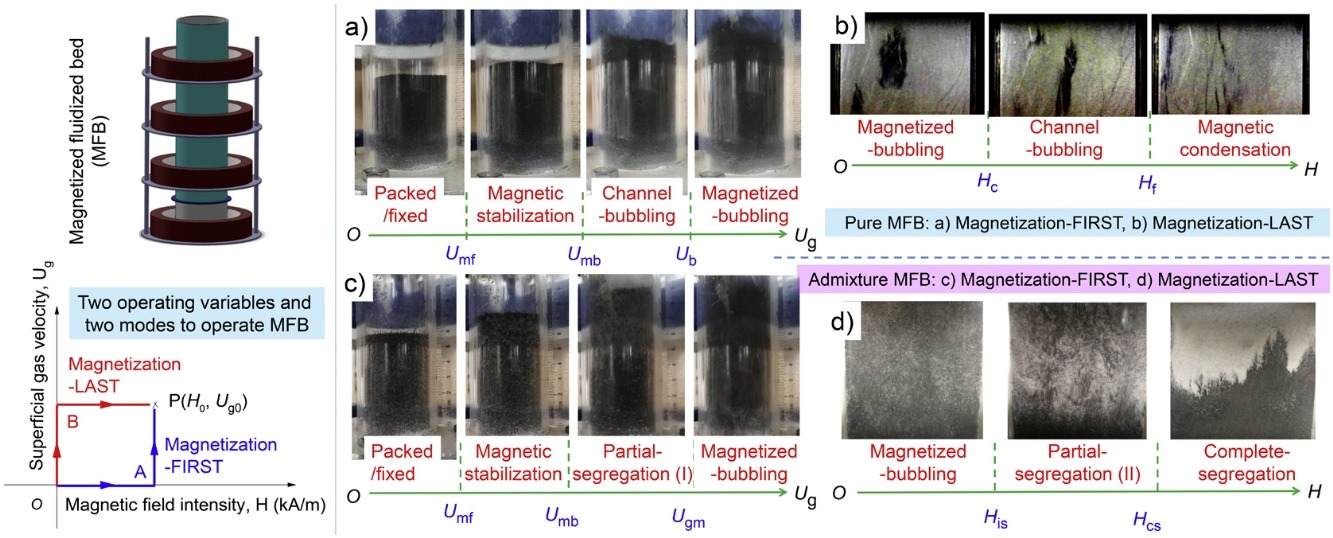
• Various flow regimes of magnetized fluidized bed (MFB) were identified.
• Methods for determining borders between two adjacent flow regimes were clarified.
• MFB state also depended on the operation mode with certain operating zones.
• MFB could be polymorphic due to internal friction among unfluidized particles.
• Many of the MFB states were metastable and belonged to amorphous state.
The magnetized fluidized bed (MFB) with Geldart-B particles exhibits many distinct flow regimes depending on the magnetic field intensity (H) and gas velocity (Ug). The identification of these regimes was reviewed for the MFB with magnetizable particles and that with binary admixture of magnetizable and nonmagnetizable particles. Meanwhile, methods for determining the boundaries between two adjacent flow regimes were clarified. The MFB state was found to depend not only on H and Ug but also on their application sequence (i.e., operation mode) within certain operating zones. The dependence feature arose from that the MFB therein could have different equilibrium states for the same combination of H and Ug. Furthermore, such a polymorphic characteristic of the MFB was revealed to result from the internal friction among the particles that were in unfluidized/packed state. Many of the MFB states were demonstrated to be in metastable equilibrium. Nevertheless, they differed significantly from the metastates well-known in the discipline of physical chemistry, such as supercooling and superheated. In fact, they belonged to the amorphous/glass state. This review will deepen our hydrodynamic understanding of the MFB and further promote its commercial application in the chemical and biochemical industries.