- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
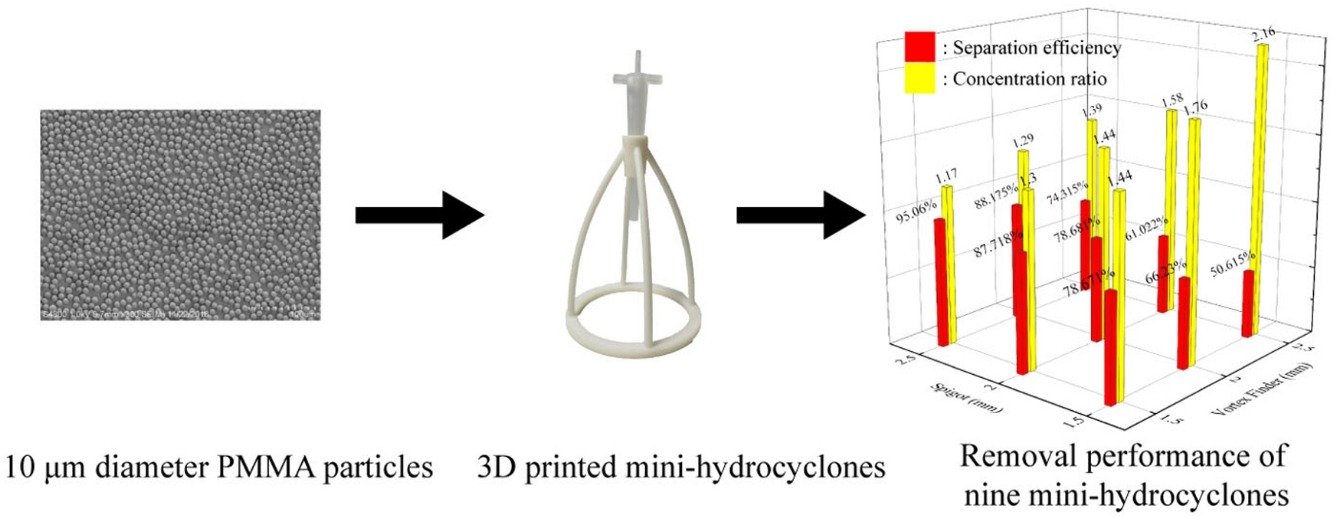
• Mini-hydrocyclones performance in removing small-size microplastics (MPs) is investigated.
• Mini-hydrocyclones are applicable to removing small-size MPs.
• Trade-off between separation efficiency and concentration ratio is observed.
• Diaeters of spigot and vortex finder affect the removal performance.
• Behaviours of small-size MPs are explained with respect to flow properties.
Large amounts of microplastics (MPs) have been found in rivers and oceans, bringing great harm to aquatic animals, plants, even human beings. However, the effective removal method of MPs, especially those with small sizes (5–20 μm) is still lacking. This work presents mini-hydrocyclones to remove 10 μm (average size) diameter MPs. The removal performance of nine mini-hydrocyclones with different diameters of spigot and vortex finder is examined experimentally and numerically. The performance of the designed cyclones is evaluated in terms of recovery, water split, concentration ratio and pressure drop. The results show that mini-hydrocyclones are applicable to removing small-size MPs with the maximum concentration ratio at 2.16 and the particle recovery at 51%. The flow characteristics inside the mini-hydrocyclones are analyzed in detail. It is shown that the distributions of water axial velocity and radial velocity could collectively affect the behaviors of small-size MPs in mini-hydrocyclones. Specifically, a larger amount of water split could entrain more fine particles to underflow. Meanwhile, a less frequent alternation of radial velocity between the positive and negative directions on the same side of the cyclone should benefit the removal of small-size MPs.