- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
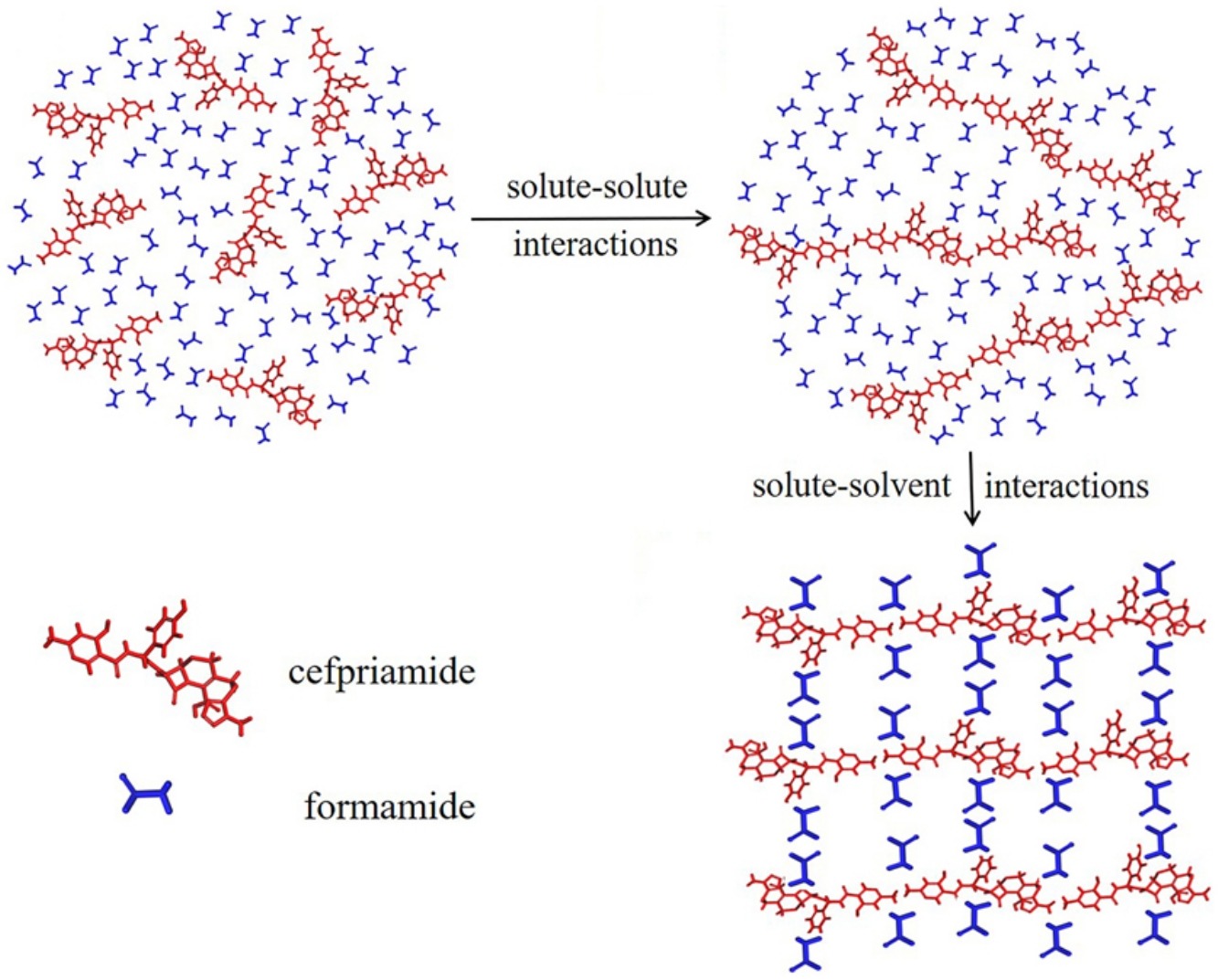
• Cefpiramide tends to form a gel in formamide solvent.
• Molecular mechanism of gel formation process is revealed.
• Strong intermolecular hydrogen bonding contributes to gel formation.
• Interactions between formamide and cefpiramide promote gel formation.
Gel is a very diverse system that has pervaded our everyday life in a variety of forms. However, the mechanism of gel formation remains ambiguous. To better understand the mechanism of gel formation, cefpiramide was selected as model compound to investigate gel formation from molecular level, with the help of experimental research and molecular dynamics simulations. Dynamic light scattering was used to detect the process of the formation of fiber aggregates by the molecules in the gel process. The results indicated that in the process of low molecular weight gels, the molecules coalesce to form a fibrous network structure to wrap the liquid. Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier Transform Infrared spectrometer and Raman spectroscopy were employed to explore the solute–solute and solute–solvent interactions, which indicated that the solvent molecules (formamide molecules) played a key role in the process of gel formation and the solute–solute interactions played a leading role. Finally, molecular dynamics simulations were employed to reveal the molecular mechanism of gel formation from molecular level.