- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
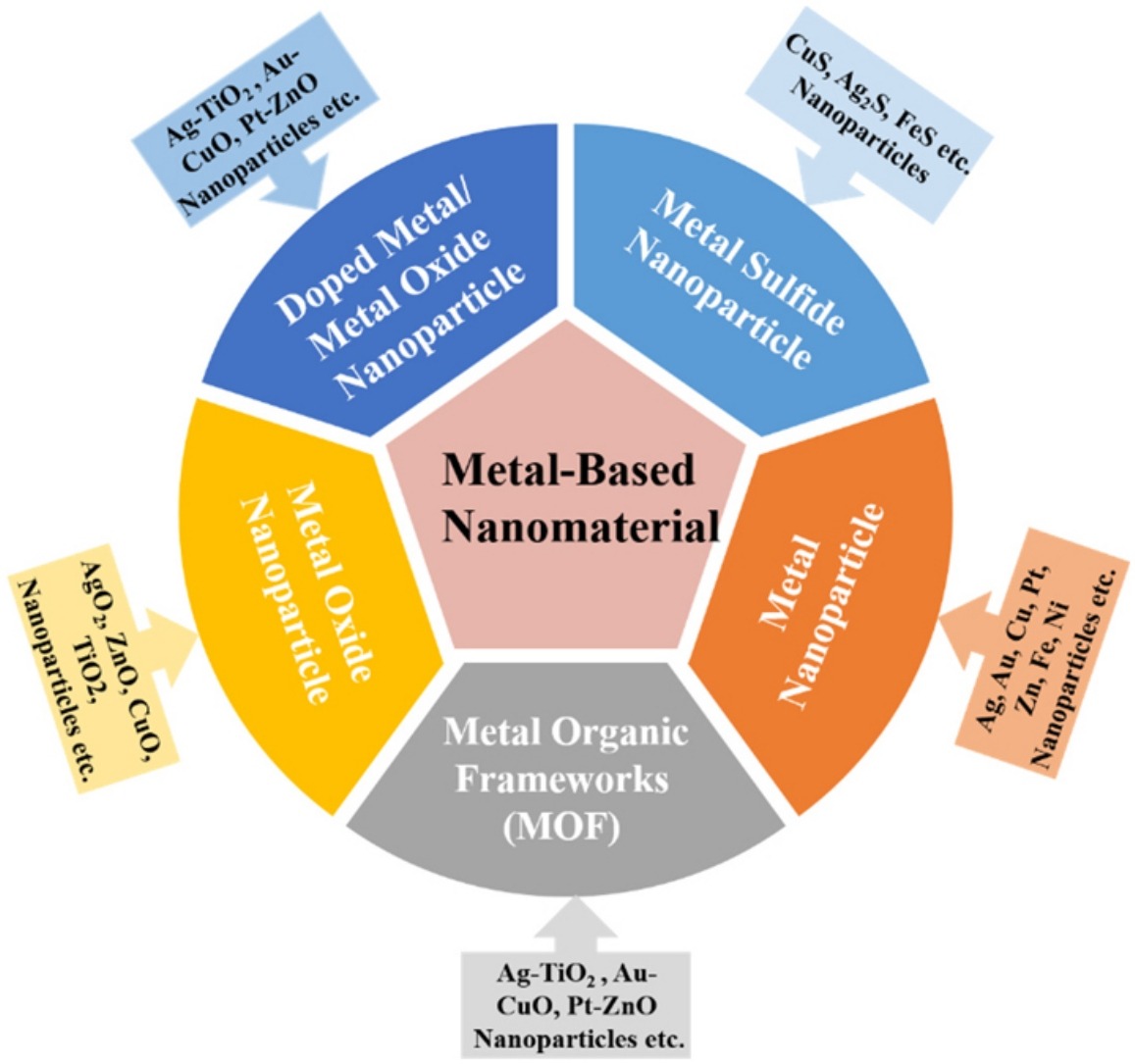
• Physicochemical and biological properties of metal-based nanoparticles and their application in cardiovascular diseases.
• Impact and optimization of metal-based nanoparticles for cardiovascular disease imaging and therapy.
• Potential risks of metal-based nanomaterial for cardiovascular disease applications.
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the most prominent cause of disability and mortality in the world. Although there have been a variety of therapeutic options for the management of CVDs, most of the traditional therapeutic strategies could not sufficiently stop or reduce the progression of these diseases and may result in some side effects. With the advance in nanotechnology, a number of metal-based nanoparticles have been developed and shown promising potentials in the treatment of CVDs. In this review, we provide a comprehensive review of researches on recent development of metal-based nanoparticles in diagnosis and therapy in CVDs as biomedical materials. We also discuss the challenges in the clinical translation and potential risks in their application of CVD therapy. Based on the ongoing research and applications, we can conclude metal-based nanoparticles are expected to become potential therapeutics for the treatment of CVDs. But their application is still in its infancy and much more efforts should be made to enforce a clinical breakthrough.