- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
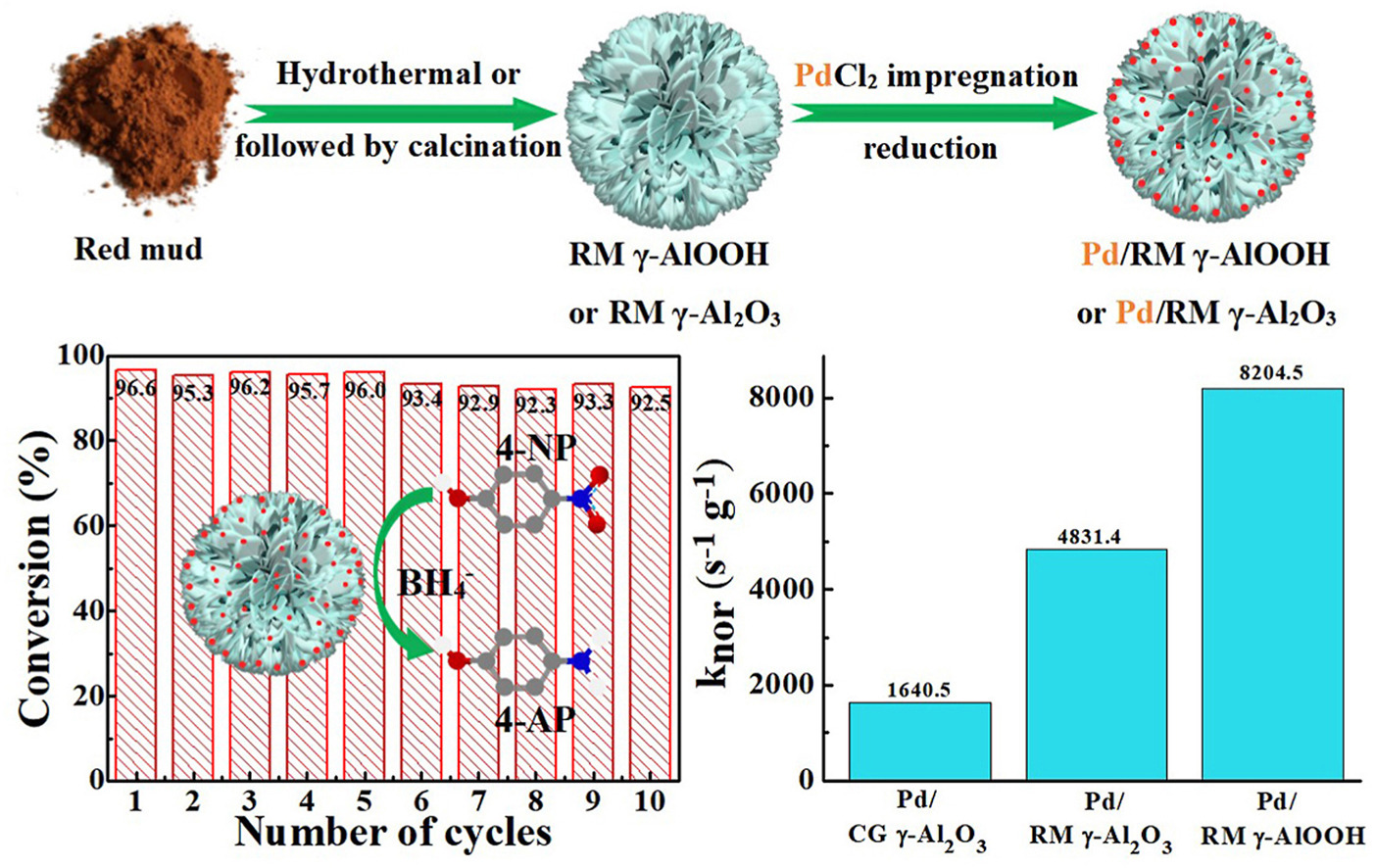
• Solid waste red mud (RM) is utilized as raw material for the disposal of the wastewater containing 4-NP.
• Uniform RM γ-AlOOH/γ-Al2O3 hierarchical porous microspheres (HPMSs) are derived from RM.
• Pd/RM γ-AlOOH and Pd/RM γ-Al2O3 HPMSs exhibit superior rate constant knor as 8204.5 and 4831.4 s−1 g−1, respectively.
• Pd/RM γ-AlOOH and Pd/RM γ-Al2O3 HPMSs both display excellent stability in 10 cycles' reduction of 4-NP.
Toward the imperative treatment of the industrial wastewater containing 4-nitrophenol (4-NP) and industrial solid waste red mud (RM), an innovative approach of "Using waste to treat waste" is developed. Valuable element Al is leached from the RM first, the resultant NaAlO2 solution is hydrothermally converted to γ-AlOOH hierarchical porous microspheres (RM γ-AlOOH HPMSs, average diameter: 2.0 μm, SBET: 77.81 m2 g−1, pore volume: 0.38 cm3 g−1) in the presence of urea. The subsequent mild thermal conversion results in γ-Al2O3 hierarchical porous microspheres (RM γ-Al2O3 HPMSs). Both of the RM γ-AlOOH and RM γ-Al2O3 HPMSs are employed as the Pd catalyst support for the catalytic reduction of 4-NP. Particularly, the as-obtained composite Pd/RM γ-AlOOH and Pd/RM γ-Al2O3 exhibit excellent catalytic activities with superior knor as 8204.5 and 4831.4 s−1 g−1, respectively, significantly higher than that of most Pd based catalysts. Moreover, the excellent catalytic stability and durability of the Pd/RM γ-AlOOH and Pd/RM γ-Al2O3 within 10 successive cycles of reduction enable the present industrial solid waste RM induced γ-AlOOH and γ-Al2O3 HPMSs as great promising Pd catalyst support for the reduction of the industrial wastewater containing 4-NP.