- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
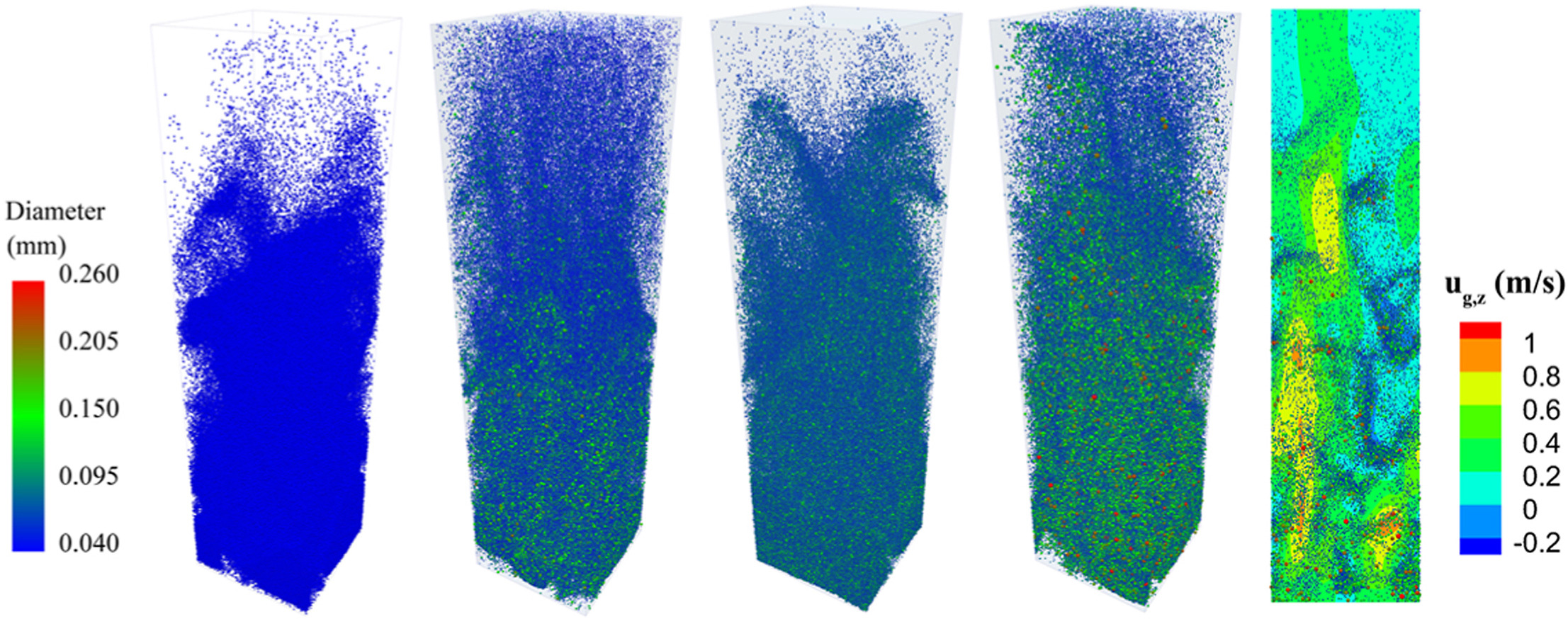
•Well-resolved CFD-DEM simulations of polydisperse gas–solid flows are performed.
•Significant impact of particle polydispersity on the gas–solid flow hydrodynamics.
•Quantifying the effect of PSD by ratio of particle size to Sauter mean diameter.
•Filtered drag models for coarse-grid CFD-DEM simulations are developed.
Particle polydispersity is ubiquitous in industrial fluidized beds, which possesses a significant impact on hydrodynamics of gas–solid flow. Computational fluid dynamics-discrete element method (CFD-DEM) is promising to adequately simulate gas–solid flows with continuous particle size distribution (PSD) while it still suffers from high computational cost. Corresponding coarsening models are thereby desired. This work extends the coarse-grid model to polydisperse systems. Well-resolved simulations with different PSDs are processed through a filtering procedure to modify the gas–particle drag force in coarse-grid simulations. We reveal that the drag correction of individual particle exhibits a dependence on filtered solid volume fraction and filtered slip velocity for both monodisperse and polydisperse systems. Subsequently, the effect of particle size and surrounding PSD is quantified by the ratio of particle size to Sauter mean diameter. Drag correction models for systems with monodisperse and continuous PSD are developed. A priori analysis demonstrates that the developed models exhibit reliable prediction accuracy.