- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
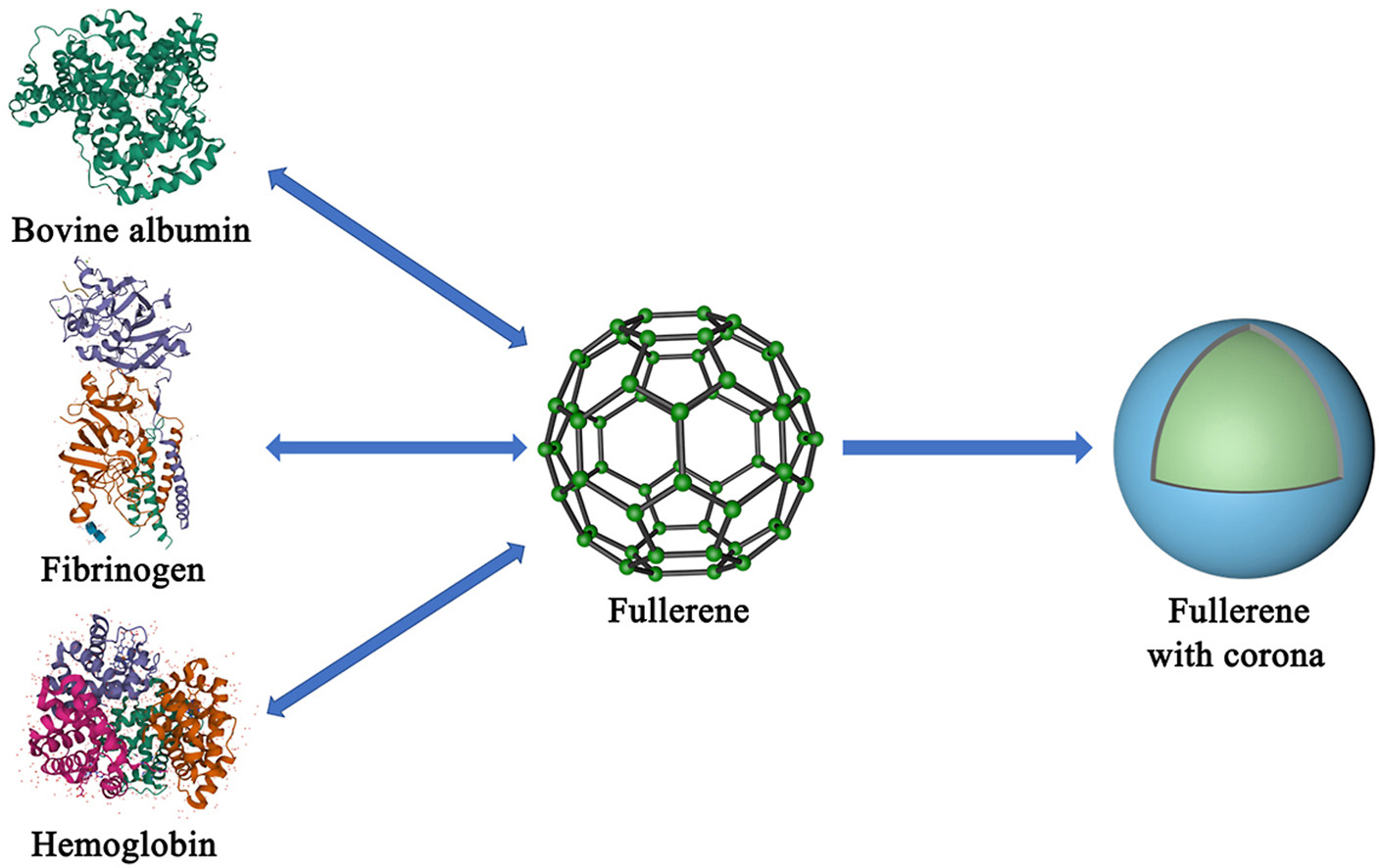
• Interaction between C60 nanocomplex and plasma proteins was investigated.
• Related binding mechanisms of C60 nanocomplex and proteins were explored.
• C60 nanocomplex induced fibrinogen to aggregate, which might cause side effects.
• C60 nanocomplex could induce conformational changes of different proteins.
Protein corona refers to the structure composed of biomolecules adsorbed on the surface of nanomaterials. The study on the effect of the interaction between protein and nanoparticles can provide an important guide for the application of nanodrug delivery. To provide a reference for the research on fullerene (C60) nanocomplex drug delivery systems, this work studied the interaction between C60 nanocomplex and a variety of plasma proteins. Research showed that the protein binding with C60 nanocomplex did not change the charge properties of protein. The proteins induced the aggregation of C60 nanocomplex. The circular dichroism spectra showed that the secondary structure of the proteins changed after binding to C60 nanocomplex. The ultraviolet–visible spectra showed that the effect of C60 nanocomplex on proteins was concentration-dependent. The fluorescence spectra showed that C60 nanocomplex could intrinsic fluorescence alteration of proteins. The adsorption capacity of C60 nanocomplex to proteins was changed at 0 h and 4 h. The interaction between nanocomplex and proteins might affect the morphological characteristics of nanocomplex and the conformation of proteins. This work could provide a reference for the research and development of C60 nanocomplex and other carbon-based nanocomplex as nanoparticulate drug delivery systems.