- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• Aggregation-induced emission (AIE) nanoparticles sparkle in the field of biomedicine.
• Near-infrared fluorophores share the merits of high penetration depth.
• Different nanocarriers endow AIE-active nanoparticles versatile functionalities.
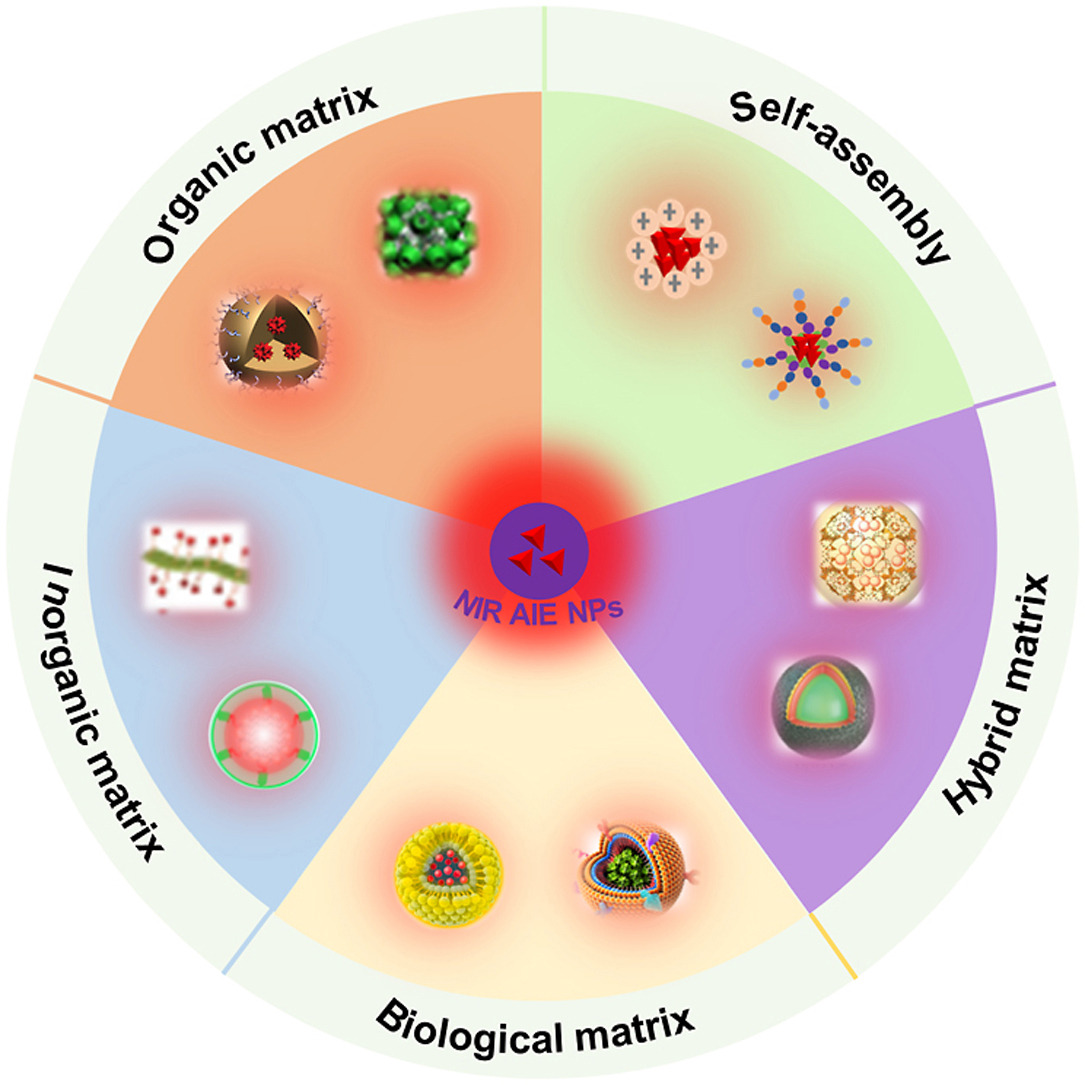
Fluorescent imaging based on near-infrared (NIR) fluorophores has revolutionized the techniques employed for detecting biological events in depth owing to their advantages referring to diminished photon scattering, high signal-to-noise ratio and better light transparence through tissue. As for conventional luminogens, the nanofabrication of those innately hydrophobic π-conjugated architectures into water-dispersible nanoparticles (NPs) may result in attenuated fluorescent intensity deriving from the detrimental distribution of π-π interactions in the confined space. Oppositely, chromophores possessing aggregation-induced emission (AIE) characteristics emit boosted brightness at aggregate level according to the mechanism of restriction of intramolecular motion (RIM). In this review, we summarize the recent progresses of NIR emissive AIE NPs for multifarious biomedical applications from the viewpoint of different fabricated manners, mainly covering self-assembly and matrices assisted approaches. Furthermore, the current challenges and future research directions of NIR AIE NPs are briefly discussed.