- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
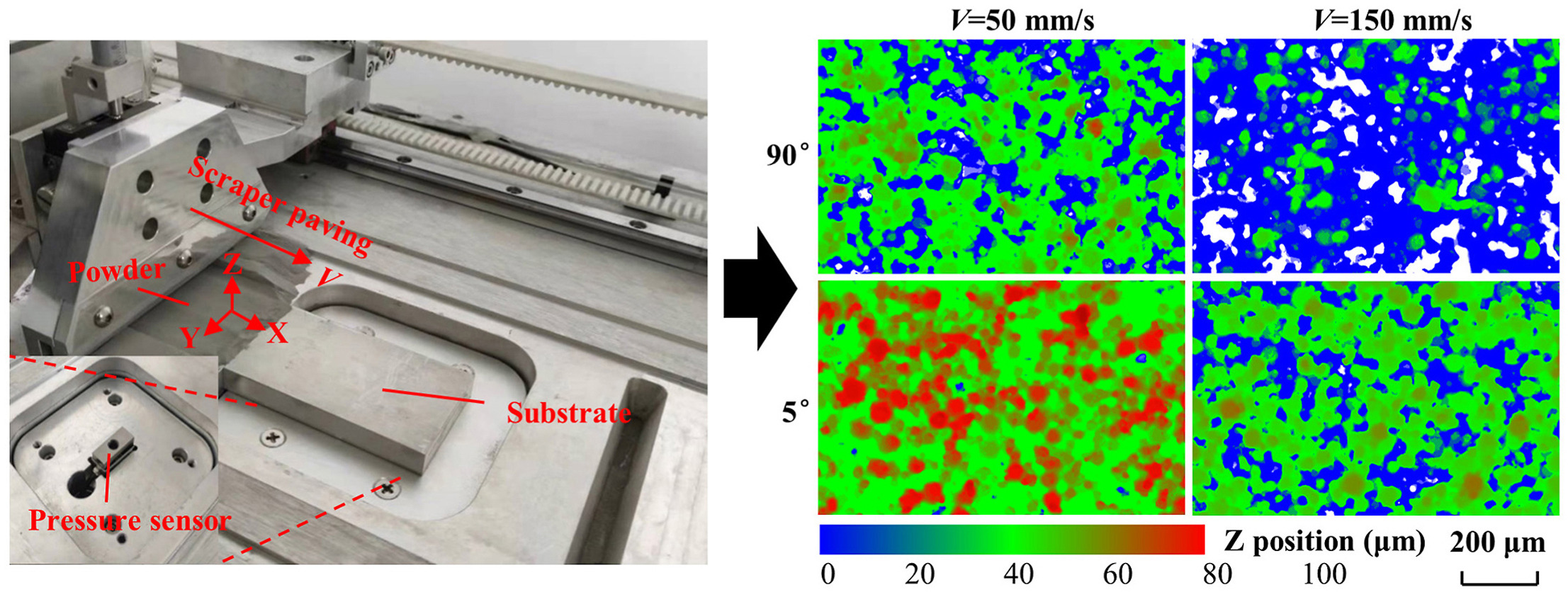
• In-situ experimental tests are performed to investigate powder paving process for the first time.
• Powder bed qualities and pressure on the substrate are directly measured in-situ.
• Reducing inclination angle can significantly increase the powder bed packing quality.
• Scraper with smaller inclination angle can be used to improve paving efficiency.
In this work, in-situ experimental tests are first performed to investigate the powder spreading process of additive manufacturing, where different kinds of scrapers and spreading speeds are employed. Detailed kinetic behaviours of individual powder particles are discussed by discrete element method simulations. It is found that the decrease of inclination angle of the scraper improves the powder pressure and compaction in the spreading process, leading to a denser powder flow and thus a denser powder bed. The increase of spreading speed also improves the powder pressure and compaction in the spreading process. However, the powder flow becomes looser due to the volume dilation, and thus the quality of the paved powder bed decreases. In industrial applications, if the higher powder spreading speed is employed to improve the processing efficiency, the scraper with a smaller inclination angle can be used to ensure the powder bed quality.