- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• ZnFe-LDO/Co3O4 was prepared by microwave hydrothermal and hydrothermal method.
• p-n heterojunction was obtained between ZnFe-LDO and Co3O4.
• ZnFe-LDO/Co3O4 heterojunction exhibited higher photoelectrocatalytic degradation.
• ZnFe-LDO/Co3O4 can be conveniently reused with a stable performance.
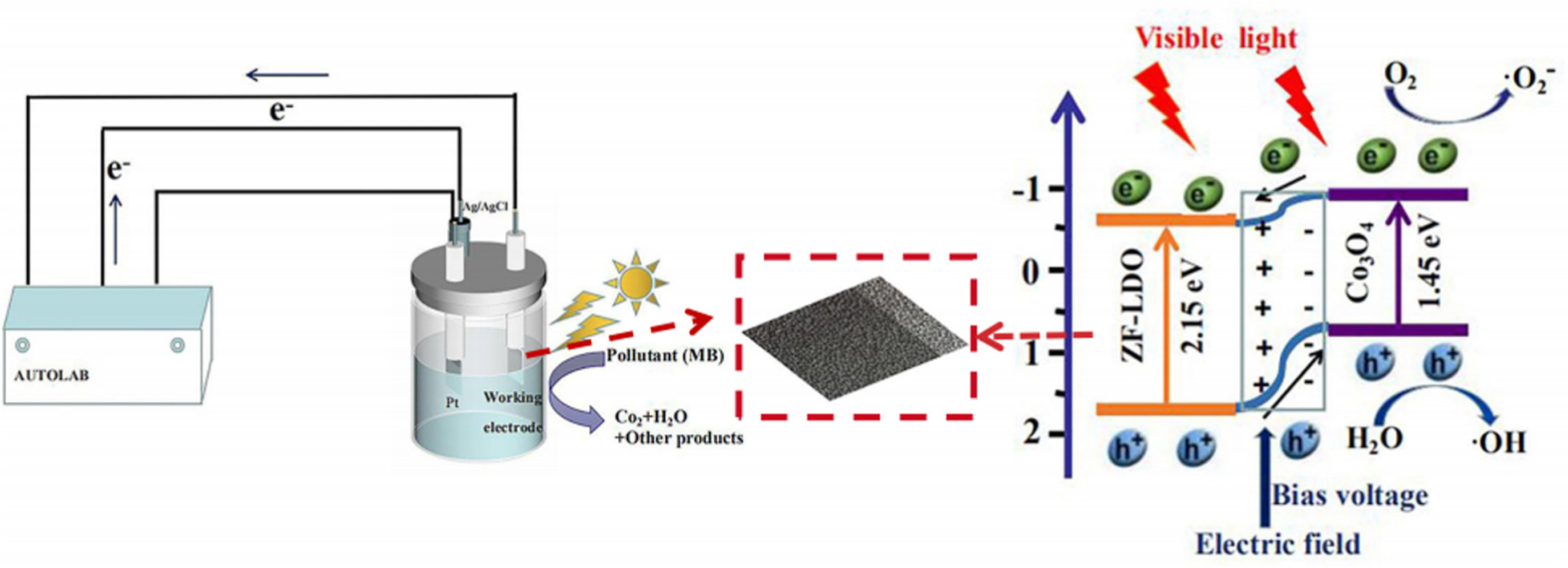
A visible light-active photoelectrocatalyst, ZnFe-layered double oxide (LDO)/cobalt(II,III) oxide (Co3O4) composites were obtained by calcining the Co loaded ZnFe-layered double hydroxide (LDH) prepared by a hydrothermal and microwave hydrothermal method. The morphological studies revealed that the ZnFe-LDO/Co3O4 composites exhibited a flower-like structure comprising Co3O4 nanowires and ZnFe-LDO nanosheets. Further, when the mass ratio of Co(NO3)2·6H2O/LDH was 1:1.8 and the calcination temperature was 550 °C, the ZnFe-LDO/Co3O4 composite exhibited 93.3% degradation efficiency for methylene blue (MB) at the applied voltage of 1.0 V under visible light after 3 h. Furthermore, the Mott-Schottky model experiments showed that the formation of a p-n heterojunction between ZnFe-LDO and Co3O4 could effectively inhibit the recombination of electrons and holes in the photoelectrocatalytic process. Meanwhile, free radical scavenging experiments showed that the active radicals of ⋅OH played an important role in the degradation of MB. Therefore, the photoelectrocatalytic effect of ZnFe-LDO/Co3O4 provides a simple and effective strategy for the removal of organic pollutants.