- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
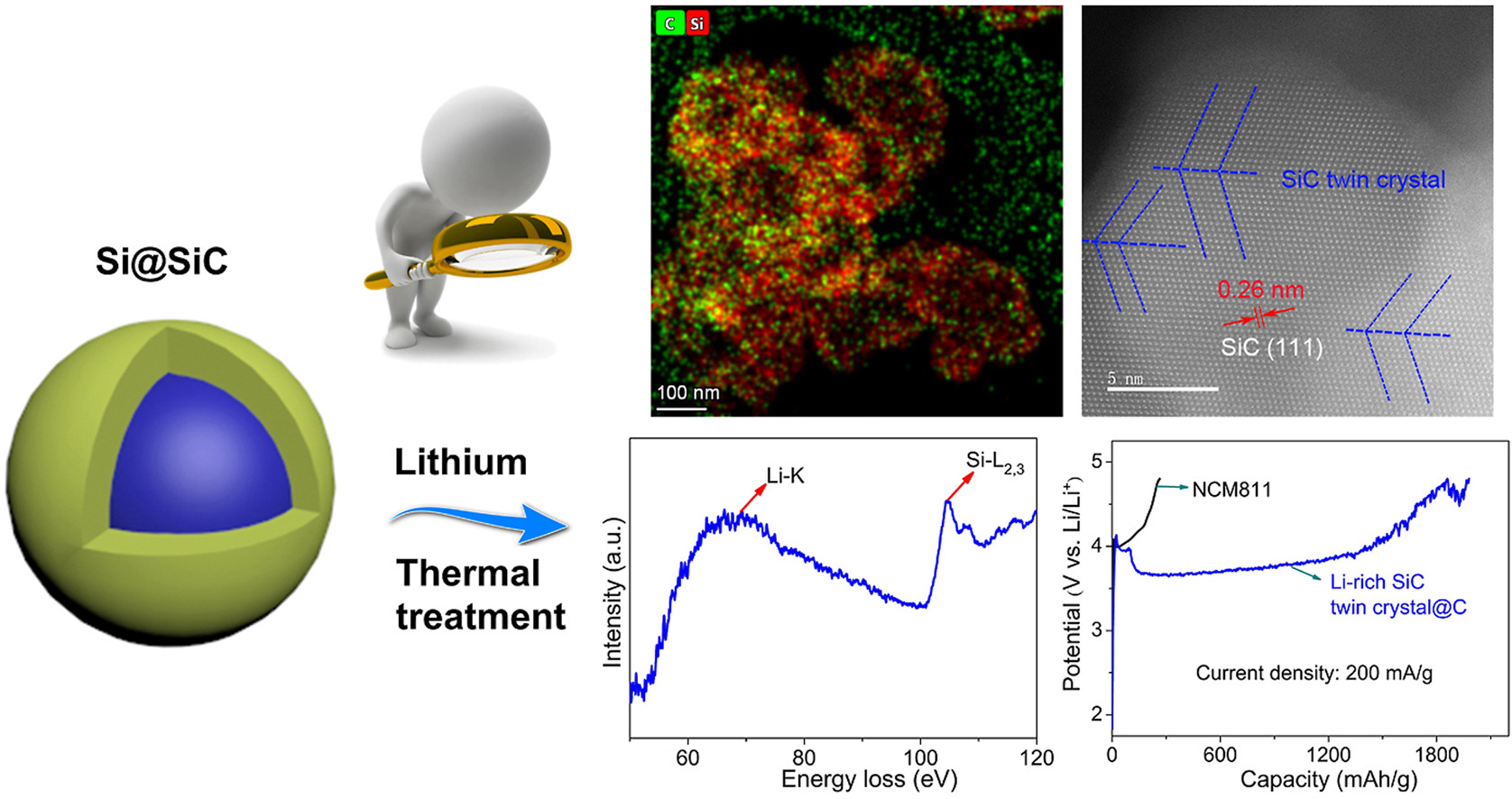
• Li has a discernible effect on the core-shell structured Si@SiC.
• Li easily inserts into the (111) plane of SiC in the presence of Si.
• A well-organized Li-rich SiC twin crystal is formed.
• This Li-rich SiC twin crystal can be a promising candidate for application in high-capacity Li-ion batteries cathode.
• Si-induced Li insertion contributes to the changes in the surface species and structure of pristine SiC.
The energy density of Li-ion batteries is closely related to the capacity and average voltage of cathode materials. Unfortunately, current cathode materials either have low capacity or voltage, which limits the development of high-energy-density Li-ion batteries. This has given challenge to many attempts to develop new cathode materials with high capacity and voltage. In this study, we find that Li easily inserts into the (111) plane of SiC in the presence of Si, and a well-organized Li-rich SiC twin crystal is formed. Ultraviolet–visible diffuse reflectance spectra and electrochemical test results suggest that this Li-rich SiC twin crystal possesses the band gap energy of 3.5 eV and charging capacity of 1979 mAh/g at the current density of 200 mA/g, making it a promising candidate for the cathode material in high-capacity Li-ion batteries. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy results reveal that Si-induced Li insertion contributes to the changes in the surface species and structure of pristine SiC. These findings suggest that the Li-rich SiC twin crystal raises new possibilities for the development of high-capacity cathode materials and merits further investigation to expand its application scope.