- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
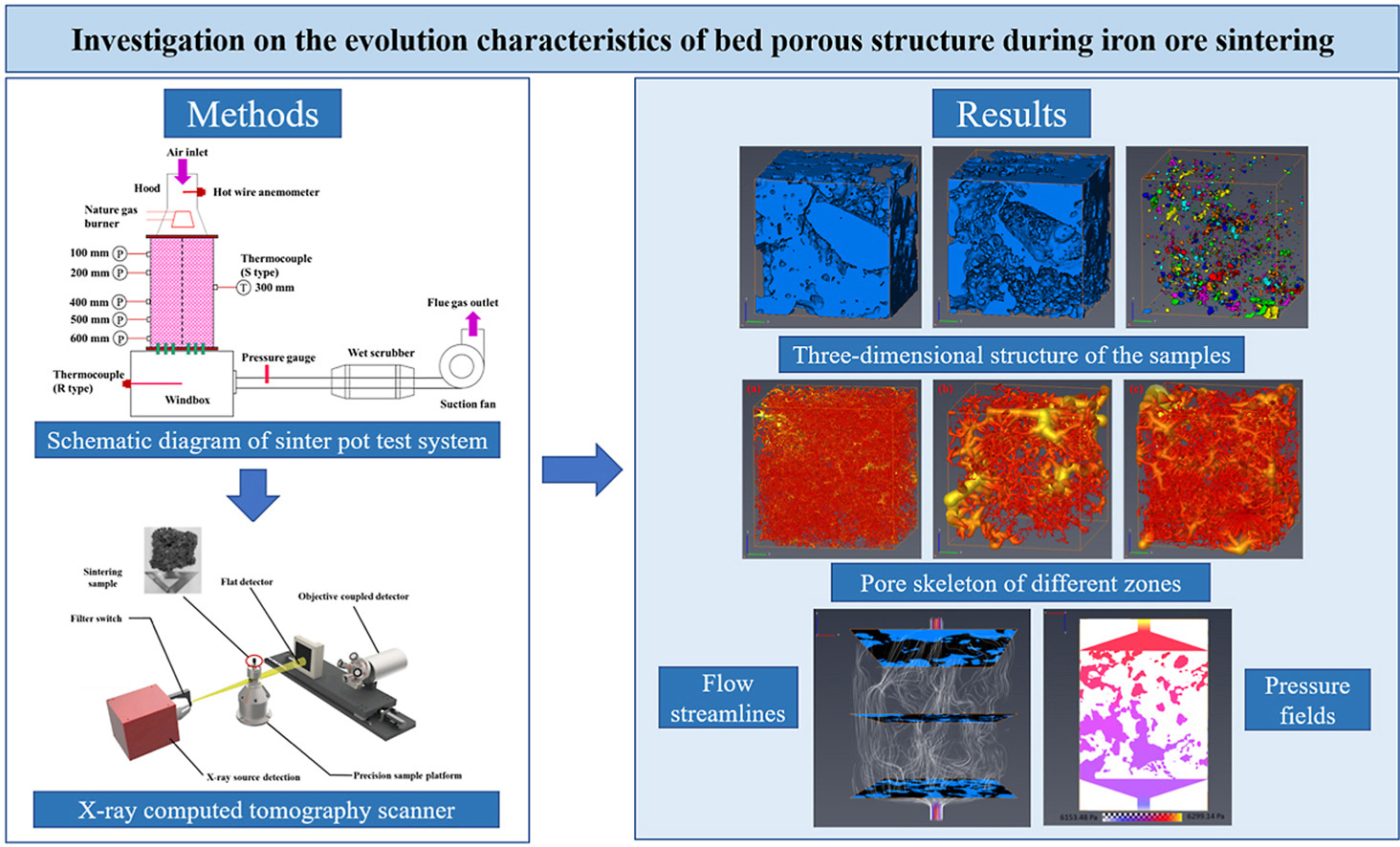
• X-ray computed tomography technology was used to analyze pore parameters.
• Pore skeleton structure model was established.
• Absolute permeability of different areas was calculated through simulation.
• Streamline and pressure drop distribution were calculated and analyzed.
• Evolution characteristics of pore structures were analyzed.
To better understand the evolution characteristics of bed porous structure during iron ore sintering, X-ray computed tomography scanning technology was used to analyze the pore parameters in different areas of the sintering bed. A pore skeleton structure model was established to study the characteristics of the airflow channels in different zones. The absolute permeability of different areas was calculated through simulation, and the corresponding streamline and pressure drop distribution were analyzed. The results show that the porosity of raw material zone, high-temperature zone, and sintered zone increases gradually, which are 37.69%, 46.41%, and 55.57%, respectively. The absolute permeability calculation results of the raw material zone and sintered zones are 792.49 μm2 and 20560.80 μm2, while the tortuosity is 1.77 and 1.45, respectively. Compared with the raw material zone, the flow streamline in the sintered zone is thicker and denser, the airflow resistance and the pressure drop are minor.