- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
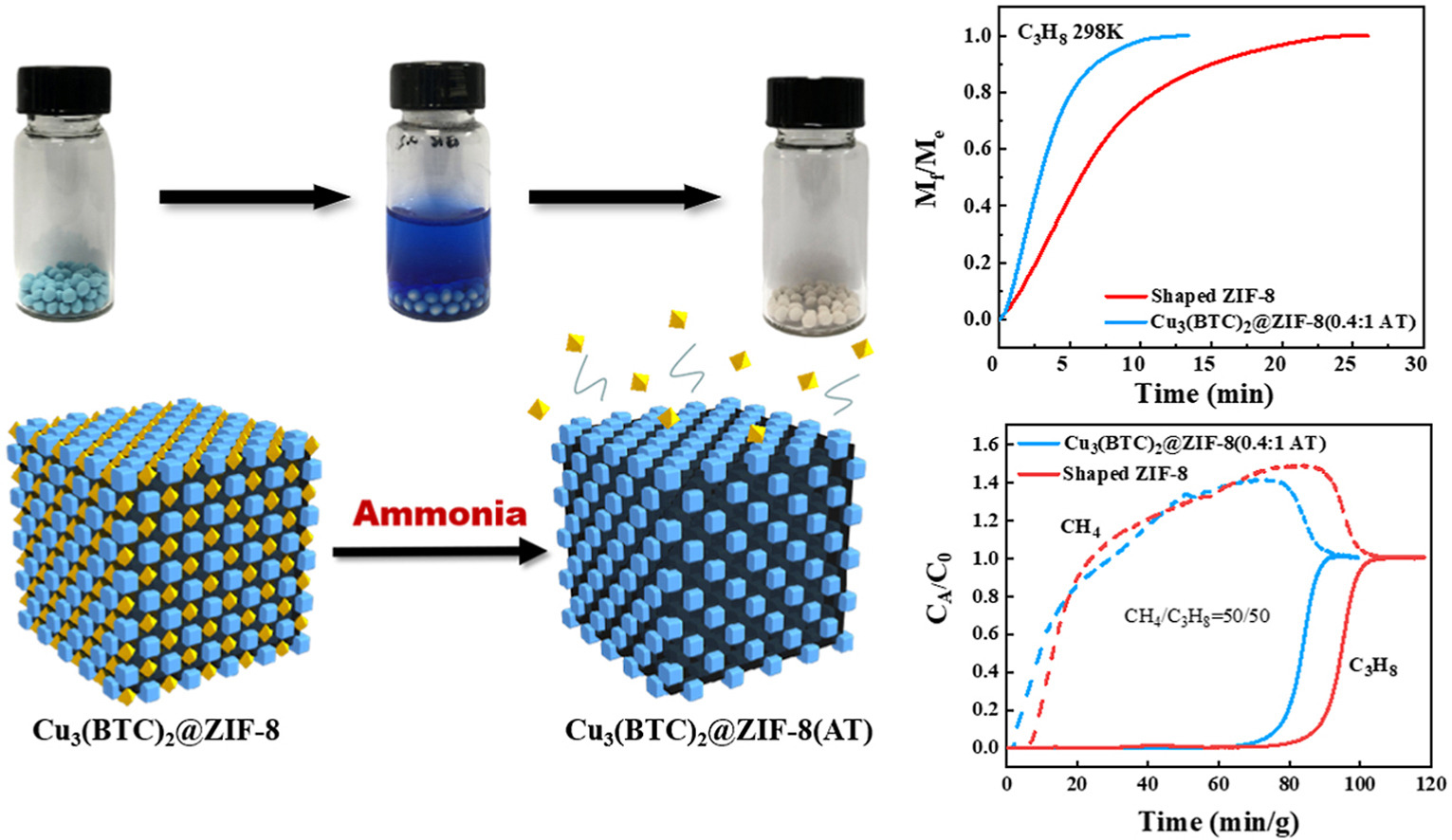
• A facile strategy was proposed for fabricating hierarchical pores in MOF pellets.
• Introduced tunable meso-/macropores in the shaped ZIF-8 spheres during the molding process.
• Pelletization with methyl cellulose binder endowed the pellets excellent mechanical stability.
• Adsorption kinetics and separation performance of HP-MOF pellets were improved significantly.
Increasing the mass diffusion efficiency is a major challenge in the realm of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). Construction of hierarchically porous, typically microporous MOF adsorbents or catalysts is crucial for enhancing both mass transfer and molecular accessibility. Many strategies have been proposed for the synthesis of hierarchically porous MOFs (HP-MOFs), with some striking results. In this paper, we proposed a facile and versatile strategy, termed the MOF-Template strategy, for fabricating hierarchical pores in MOF particle. The highly controlled crystalline sizes and morphologies of the unstable Cu-MOFs Cu3(BTC)2 and Cu(Qc)2 have been exploited in their utilization as sacrificial agents by uniformly dispersing them during the shaping process of ZIF-8. Through a facile treatment with alkaline solution, tunable mesopores and macropores could be easily introduced in the shaped ZIF-8 spheres. This strategy could effectively improve the adsorption kinetics and separation productivity of MOF materials while maintaining high mechanical stability, offering promising prospects for industrial application.