- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
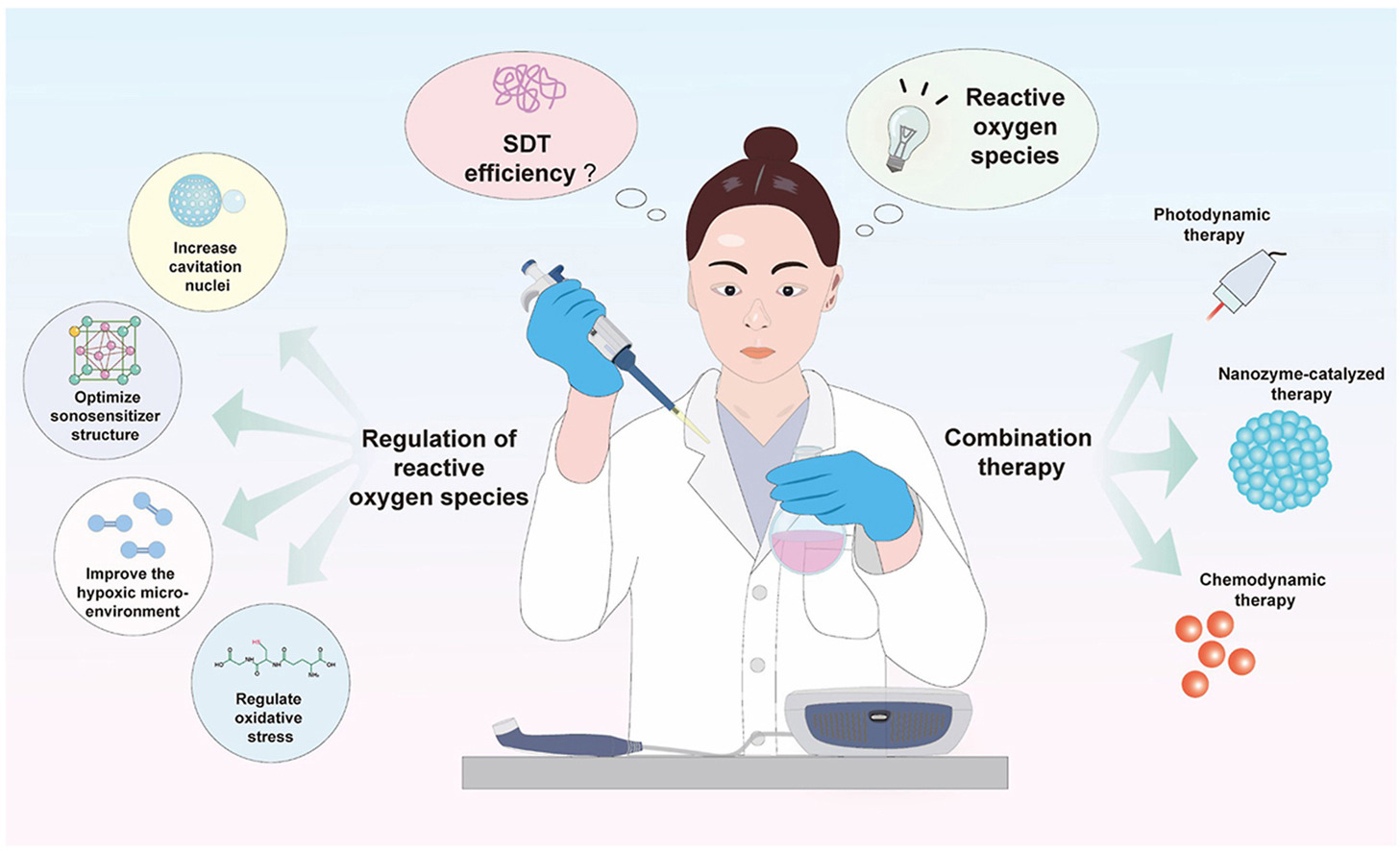
• Reactive oxygen species play an important role in sonodynamic therapy.
• The generation mechanisms of reactive oxygen species in sonodynamic therapy.
• The regulatory strategies of reactive oxygen species in sonodynamic therapy.
• Sonodynamic therapy combined with other treatment modalities based on reactive oxygen species.
Reactive oxygen species (ROS), involving in many biological reactions, play an important role in disease treatment. Among the various ROS-based therapeutic modalities, sonodynamic therapy (SDT) stands out with its unique advantages. In turn, the SDT efficacy is mainly dependent on the ROS levels in the disease microenvironment. Therefore, in recent years, researchers have extensively investigated SDT with high ROS generation capacity. In this review, we focus on effective strategies to improve the therapeutic efficiency of SDT by modulating ROS, overview the basic mechanisms of ROS generation by sonosensitizers, highlight the rational design of sonosensitizers, and summarize strategies to improve the SDT efficacy by modulating disease microenvironment. In addition, multiple ROS synergistic treatment modalities and the prospect of SDT are discussed. We believe that the understanding and exploration of SDT enhancement strategies will facilitate the clinical translation of SDT.