- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
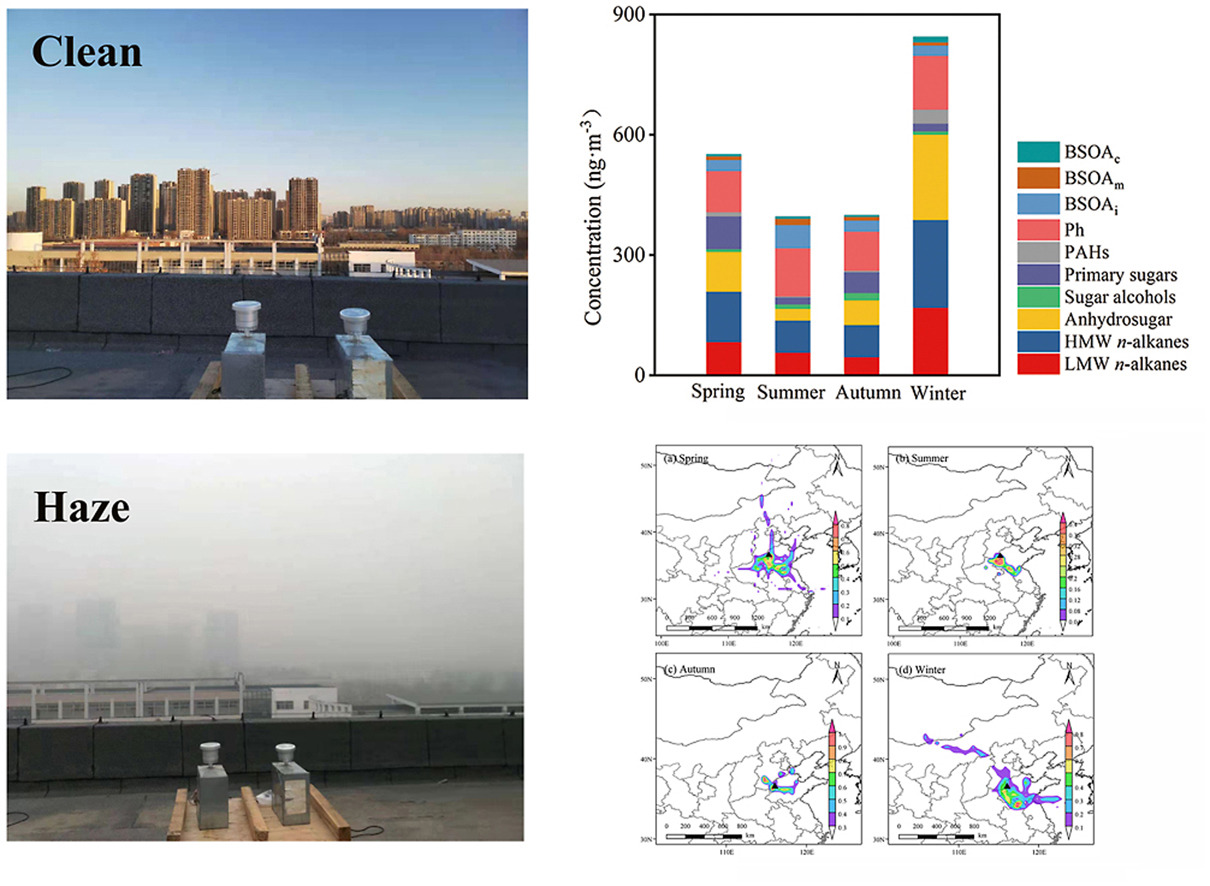
• Primary organic markers exhibit the highest concentrations in winter.
• Biogenic secondary organic aerosol (BSOA) present the highest value in summer.
• Combustion sources contributed more to organic aerosol (OA) in cold seasons.
• The secondary oxidation made up more in the warm seasons.
• Biomass burning was an important contributor to OA in winter.
To better understand the seasonal characteristics of urban organic aerosol (OA) in the North China Plain (NCP), PM2.5 samples in the urban atmosphere of Liaocheng were collected and analyzed. The molecular distribution of the organic markers in the urban atmosphere of Liaocheng reveals that n-alkanes (39.3%) was the most abundant species all year round, followed by saccharides (28.2%), phthalic acids (Ph, 20.8%), biogenic secondary organic aerosol (BSOA) tracers (9.4%), and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAHs, 2.3%). PM2.5, organic carbon (OC), elemental carbon (EC), and primary organic markers exhibit the highest concentrations in winter, due largely to the increased biomass burning and coal combustion for house heating in local and surrounding regions. However, the concentration and relative abundance of BSOA are significantly higher in summer than other seasons, induced by the more favorable meteorological conditions that would promote the emissions of biogenic volatile organic compounds (BVOCs) and the secondary production of BSOA. The ratios of OC/EC and 3-methyl-1,2,3-butanetricarboxylic acid to cis-pinic acid plus cis-pinonic acid (MBTCA/(PA + PNA) are higher in the warm seasons than those in the cold seasons, indicating that the oxidation of OA is sensitive to air temperature. Compared to 2017, the concentration level of PAHs during wintertime decreased by 40.8%, confirming that the stringent regulation of coal burning is effective. The highest concentration of high molecular weight (HMW) n-alkanes and three anhydrosugars in winter, and the close correlation of levoglucosan with HMW n-alkanes suggests that the impact of biomass burning was more significant in winter. The same seasonal characteristic of the ratios of high-/low-NOx products with NOx and the strong correlation of high-/low-NOx products with levoglucosan indicate that the formation of isoprene SOA (SOAI) tracers was significantly influenced by anthropogenic emissions. The molecular compositions, the distributions of fire spots, backward trajectories of air masses, and correlation analysis suggest that air pollution events in spring were primarily resulted from biomass burning and secondary oxidation, while pollution events in winter were largely driven by the increased combustion sources, and promoted aqueous secondary formation. Our results suggest that the reduction of biomass and coal combustion should be taken into account to improve the urban air quality in the NCP.