- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
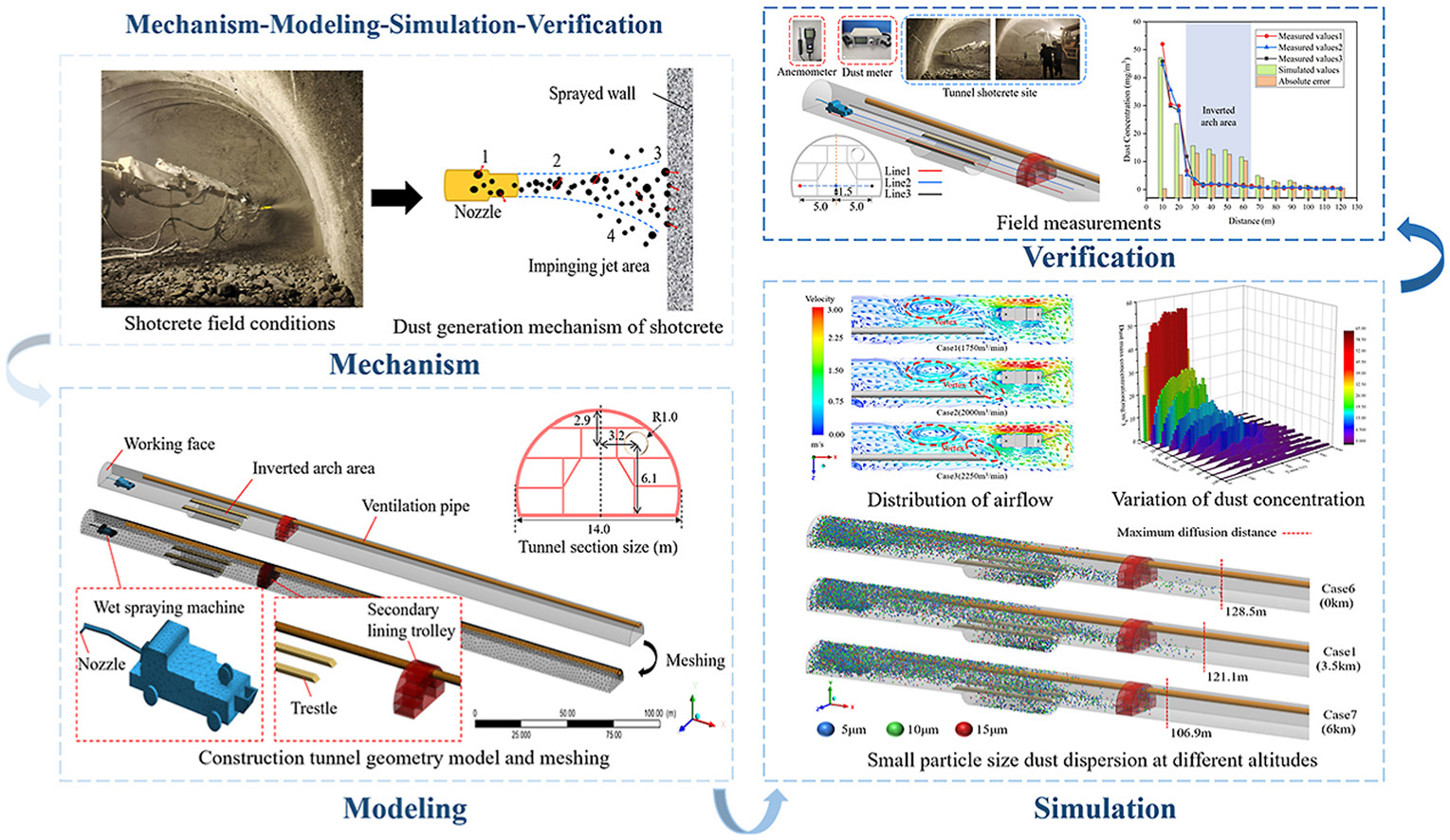
• The dust production mechanism of shotcrete was summarized.
• The dynamic diffusion of dust under different conditions was visualized.
• The movement law of fine dust particles in high-altitude tunnels was analyzed.
• The correlation values of the influencing factors on dust diffusion were investigated.
The surrounding rock needs shotcrete support after drilling and blasting excavation in the tunnel; the high concentration of dust generated in the process will endanger workers’ occupational health. Therefore, to ensure the cleanness and safety of the tunnel construction process, a full-scale model of the tunnel was established based on field data of a high-altitude tunnel of the Sichuan-Tibet railway. The dust production mechanism is summarized by combing the whole process of shotcrete. The Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) method was used to study the diffusion and transport of dust under different conditions. The grey relational analysis was applied to investigate the correlation values of the influencing factors on dust diffusion in the shotcrete operation area. The results show that the dust generation mechanism of shotcrete includes the sudden change of particle velocity in the jet area leading to escape and particle impact dust generation, where fine dust is easily dispersed in the tunnel. During continuous dust production, the dust concentration is higher near the wet spraying machine and on the backflow side of the working face. Increasing the air supply volume and shortening the distance between the air duct and the working face is conducive to diluting the dust concentration in the tunnel. In the high-altitude environment, the dust concentration in the tunnel decreases, the diffusion distance becomes smaller, the settlement proportion of dust particles increases, and the risk of secondary pollution increases. The simulation results and the field measurement data are consistent, which can provide theoretical support for the construction site dust control.