- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
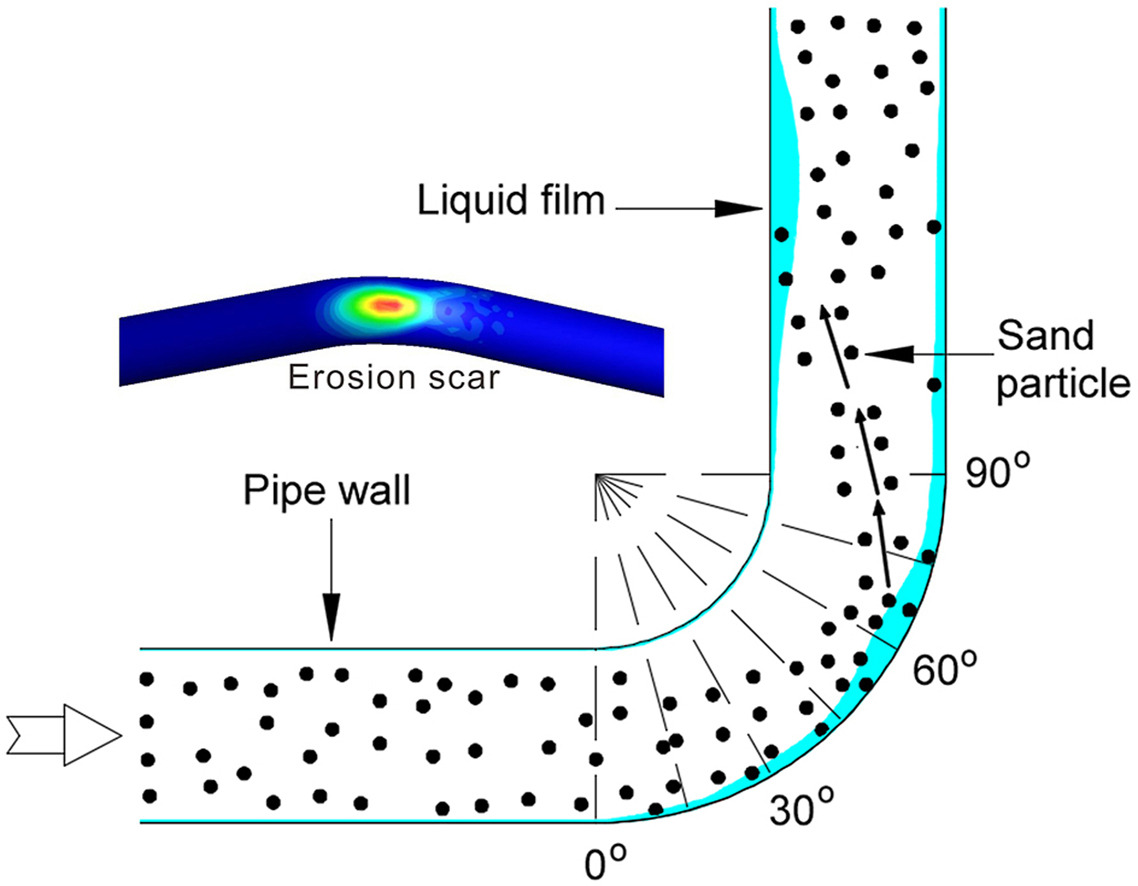
• A detachable test elbow was designed to investigate the erosion pattern.
• A CFD-based method for erosion calculation was proposed for annular flow.
• The most severe eroded area of the pipe bend was determined.
• The CFD-predicted elliptical erosion scar on the elbow was deeply analyzed.
The internal erosion of pipelines in oil and gas storage and transportation engineering is highly risky. High gas velocity of annular flow entrained sand will cause damage to the pipelines, and may further result in thinning of the wall. If this damage lasts for a long time, it may cause pipeline leakage and cause huge economic losses and environmental problems. In this research, an experimental device for studying multiphase flow erosion is designed, including an erosion loop and an experimental elbow that can test the erosion rate. The annular flow state and pipe wall erosion morphology can also be tested by the device. The computational fluid dynamics (CFD) method is combined with the experiment to further study the annular flow erosion mechanism in the pipeline. The relationship between gas-liquid-solid distribution and erosion profile was studied. The results show that the most eroded region occurs between 22.5° and 45° in the axial angle direction and between 90° and 135° in the circumferential angle direction of the elbow. The pits and deep scratches form on the surface of the sample after the sand collision.