- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
Anqi Lin a 1, Shujie Liu a 1, Hui Wei a b *
• Nanozymes have attracted considerable interests in biomedical applications.
• Nanozymes have been developed as therapeutic agents in orthopaedic diseases.
• Nanozymes shows great potential for more bone diseases along with challenges.
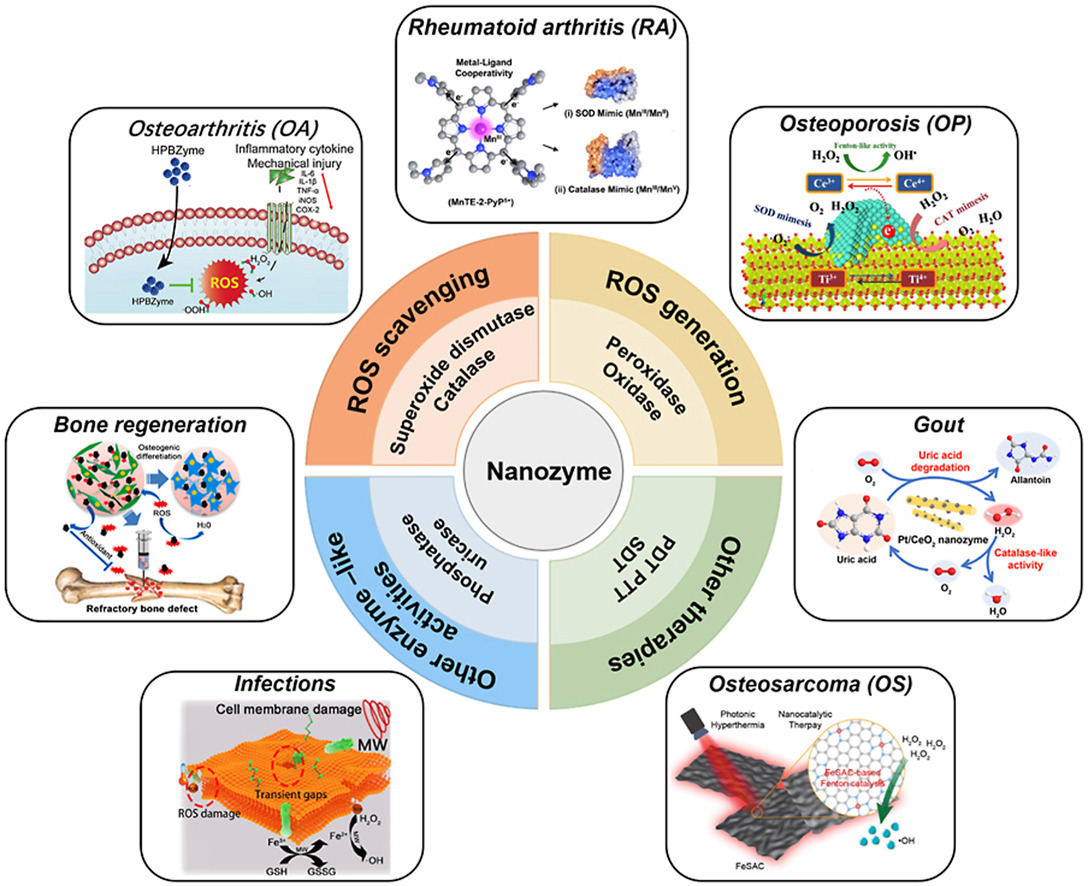
As the next generation of artificial enzymes, nanozymes have attracted increasing attention in biomedical applications due to their multienzyme-like characteristics, multifunctionalities, low cost, and high stability. By taking advantage of their diverse activities, a growing number of nanozyme-mediated therapeutic strategies have been developed for various diseases. Herein, we provide a brief review of the representative studies of nanozymes, especially in orthopaedic diseases over the past decade, which include arthritis, osteoporosis, bone regeneration, bacteria-associated infections, and osteosarcoma. Moreover, the future potential applications and some major challenges are also discussed. This review would not only provide some instructive views of nanozymes but also promote the development of enzyme-mimetic strategies in orthopaedics.