- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
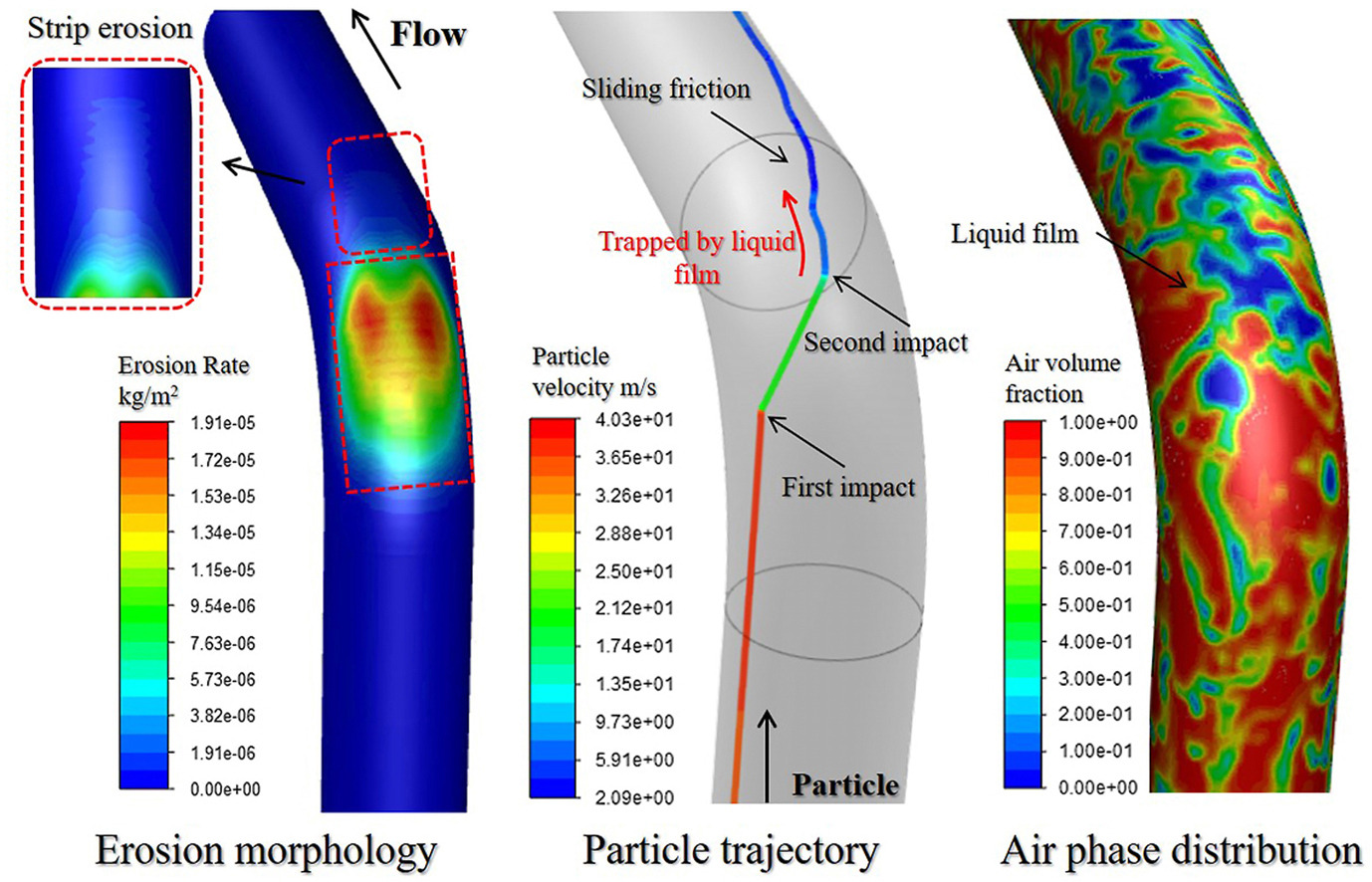
• VOF-DPM coupled numerical model for erosion prediction in annular flow was developed.
• Liquid entrainment behavior in annular flow was reasonably simulated.
• Cushion effect of liquid film was evaluated through the particle impact behavior.
• Erosion morphology generation mechanism was revealed by trajectory analysis.
Sand particle erosion is always a challenge in natural gas production. In particular, the erosion in gas–liquid–solid annular flow is more complicated. In this study, a three-phase flow numerical model that couples the volume of fluid multiphase flow model and the discrete phase model was developed for prediction of erosion in annular flow. The ability of the numerical model to simulate the gas–liquid annular flow is validated through comparison with the experimental data. On the basis of the above numerical model, the phase distribution in the pipe was analyzed. The liquid entrainment behavior was reasonably simulated through the numerical model, which guaranteed the accuracy of predicting the particle erosion. Additionally, four erosion prediction models were used for the erosion calculation, among them, the Zhang et al. erosion model predicted the realistic results. Through the analysis of the particle trajectory and the particle impact behavior on the elbow, the cushion effect of the liquid film on the particles and the erosion morphology generation at the elbow were revealed.