- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
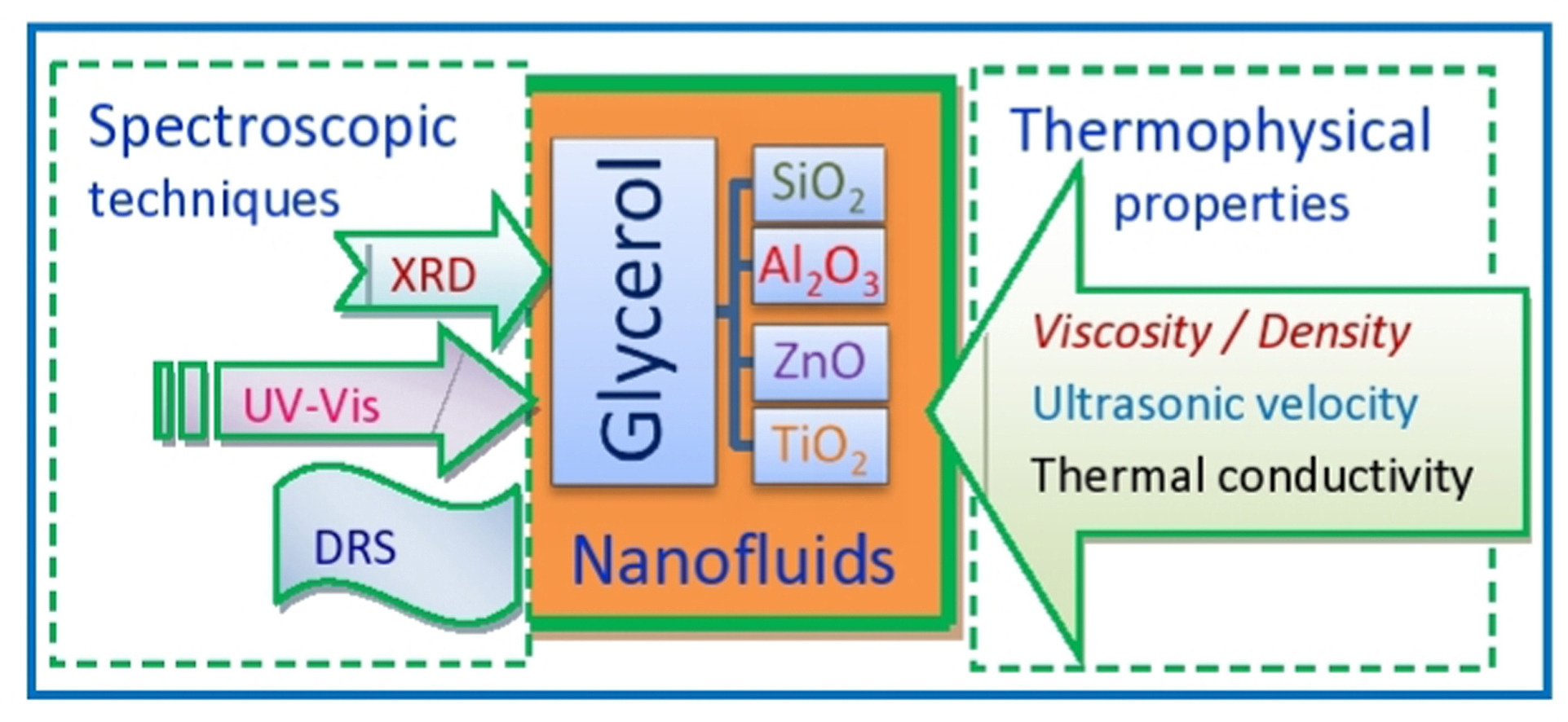
• Nanofluids of glycerol and nano oxides (TiO2, ZnO, Al2O3, and SiO2) are studied.
• Nanofluids are characterized by XRD, UV–Vis, DRS techniques and thermophysical measurements.
• Multiphysics including optical, dielectric, and acoustic parameters are provided.
• Roles of molecule-nanoparticle interaction and oxides parameters are explored.
• Multifunctional applications are listed and discussed for nanofluidics.
Nanofluid (NF) materials consisting of glycerol (Gly) and different inorganic nano oxides (TiO2, ZnO, Al2O3, and SiO2 for the oxides concentration of 0.01 wt% to the weight of Gly base fluid) were prepared by a two-step method through ultrasonic cavitation process. These nanofluids were investigated by employing an X-ray diffractometer (XRD), ultraviolet–visible (UV–Vis) spectrophotometer, 20 Hz to 1 MHz frequency range dielectric relaxation spectroscopy (DRS), ultrasonic interferometer, and rotational viscometer. The multiphysics of these nanofluids includes structural and optical properties, dielectric permittivity, electrical conductivity, conductivity relaxation, ultrasound velocity, adiabatic compressibility, acoustic impedance, viscosity, density, thermal conductivity, and viscoacoustic relaxation were characterized. The XRD patterns identified monodispersed and stable suspensions of these different characteristic nanoparticles in the hydrogen-bonded 3D supramolecular structure of ultra-high viscous glycerol fluid which were supported by their UV–Vis absorbance analyses. The energy band gap values of the TiO2 and ZnO containing nanofluids were found primarily ruled by the characteristic optical properties of these oxides nanomaterials. The complex dielectric and various electrical functions studied at 25 °C revealed that the suspension of different oxide nanoparticles in the glycerol fluid increased the static permittivity whereas reduced the direct current electrical conductivity which showed strong conductivity relaxation process dependence. The rheological measurements of the formulated nanofluids were performed over a shear rate range of 0.4–40 s−1 at temperatures of 25–55 °C. The linear relationship between shear rate and shear stress and also the shear rate-independent viscosity revealed the Newtonian behaviour of these nanofluids. The shear viscosity non-linearly decreased with the increase of temperature and exhibited the Arrhenius behaviour for all different oxides containing Gly-based nanofluids. The acoustic parameters of the nanofluids were altered unevenly with types of nano oxides and inferred some structure-property correlations. The promising technologically useable properties of these nanofluids were expected to impact their potential applications in optoelectronics, UV-blocking, sensing, nanodielectrics, energy storing and electric insulation, heat transfer systems, and also in materials processing for the development of innovative soft condensed devices.