- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
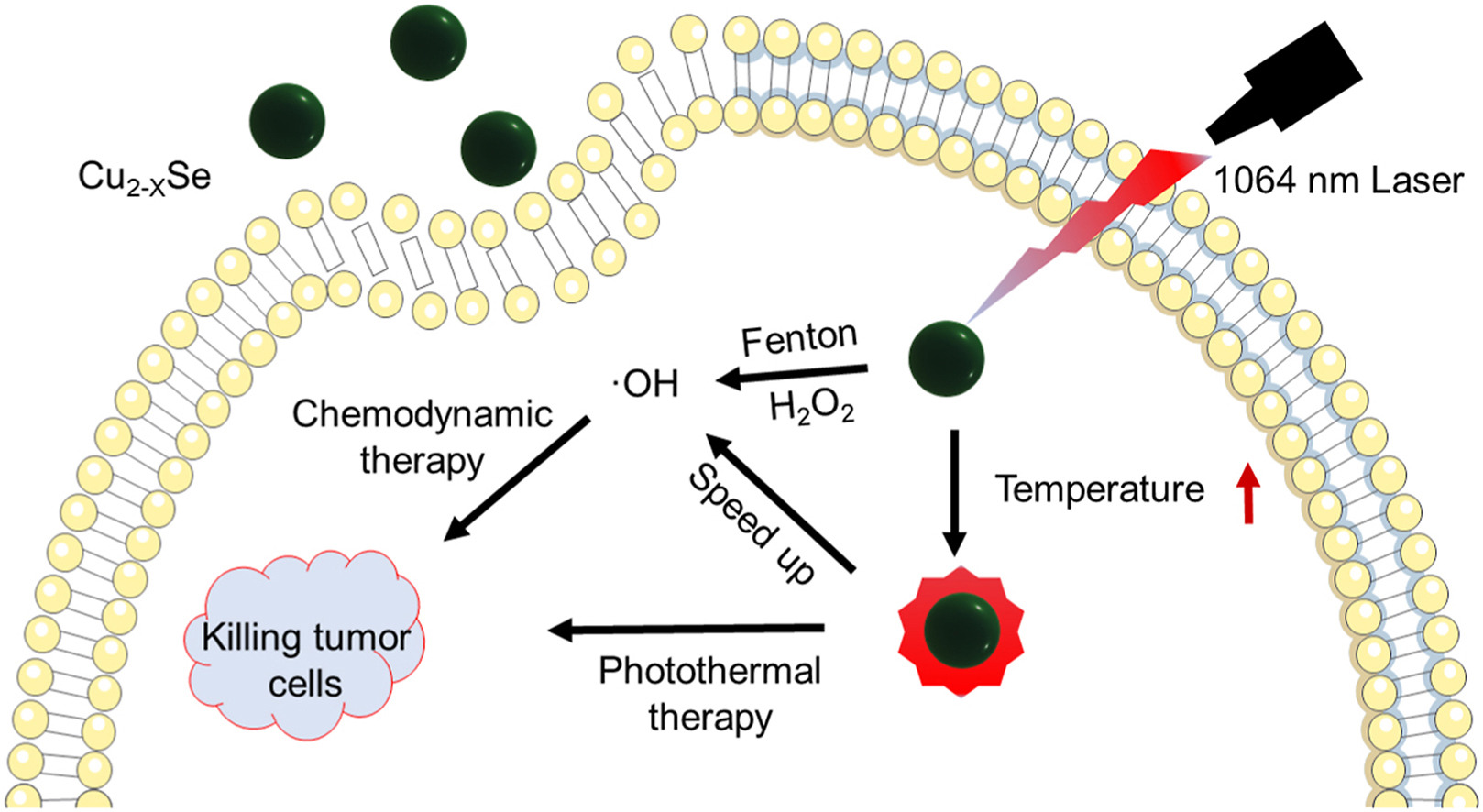
• A super-homogenous and highly dispersive spherical nanoparticle Cu2-XSe was prepared.
• Nanoprobe displayed a strong (SPR) peak in the NIR-II and high Fenton catalytic efficiency.
• Nanoprobe could effectively inhibit tumor growth and exhibit good biocompatibility.
Laser mediated photothermal/chemodynamic co-therapy is widely applied for anti-cancer treatment due to its good therapeutic effect. However, the laser wavelength for effectively targeting deep tumor tissues can decide whether or not it is a key premise of irradiation treatment. In this study, a super-homogenous and highly dispersive spherical nanoparticle Cu2-XSe was prepared, which displayed a strong surface plasmon resonance (SPR) peak in the near-infrared region (NIR)-II and high Fenton catalytic efficiency. The results of in vitro experiments showed that Cu2-XSe nanoparticles exhibited high photothermal conversion efficiency under the excitation of NIR-II laser irradiation, which significantly improved its ability to produce ·OH. In a tumor-bearing mouse model, the combination of Cu2-XSe and photothermal/chemodynamic co-therapy guided by the real-time photoacoustic imaging in the NIR-II could effectively inhibit tumor growth and exhibit good in vivo/in vitro biocompatibility. In summary, this Cu2-XSe nanoparticle-based NIR-II laser-mediated photothermal/chemodynamic co-therapy strategy is expected to provide a new option for the diagnosis and treatment of liver cancer.