- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
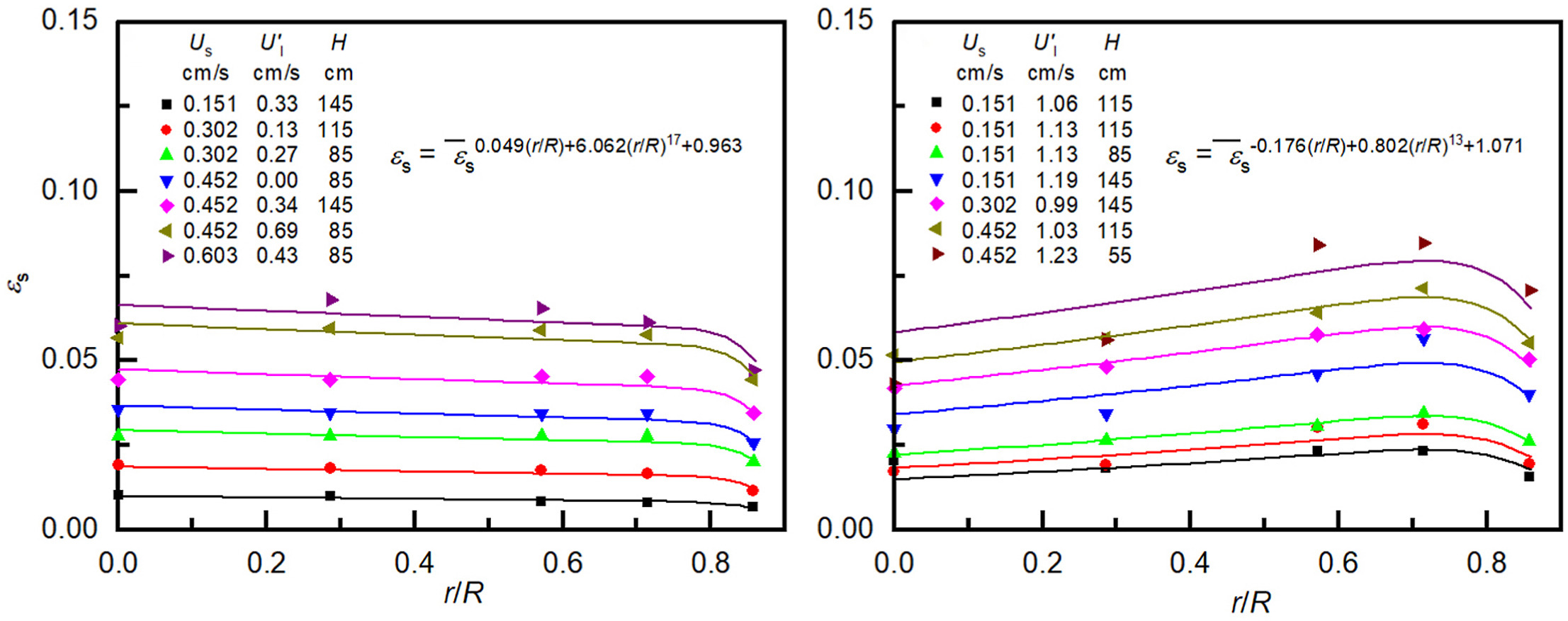
• Axial and radial distributions of solids holdup and particle velocity were investigated in a CCLSFB.
• A new flow regime map including fluidized bed, transition, and flooding regimes was established.
• A pair of correlations was proposed to predict the radial solids holdup distribution.
The local solids holdup and local particle velocity in a Countercurrent Liquid-upward and Solids-downward Fluidized Bed (CCLSFB) were investigated in details using optical fiber probes with two different models in a Plexiglas column of 1.5 m in height and 7.0 cm in inner diameter. A new flow regime map including fluidized bed, transition, and flooding regimes was established. The axial solids holdup distribution is almost uniform at low liquid velocity and/or solids flowrate and becomes less uniform with higher solids holdup at the top of the column after the operating liquid velocity is reaching the flooding velocity. The radial solids holdup profile is also nearly flat with a slightly lower solids holdup in the near-wall region at low liquid velocity and solids flowrate but becomes nonuniform as the operating liquid velocity approaches the flooding velocity. Two equations were also proposed to correlate radial local solids holdups. The descending particle velocity in CCLSFB increases with the decrease of the liquid velocity and the increase of the solids flowrate. A generally uniform particle velocity distribution was found in the axial direction, as well as in the radial direction except for a small decrease near the wall. These results on the local solids flow structure would provide basic information and theoretical supports for the design and industrial application of CCLSFB.