- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
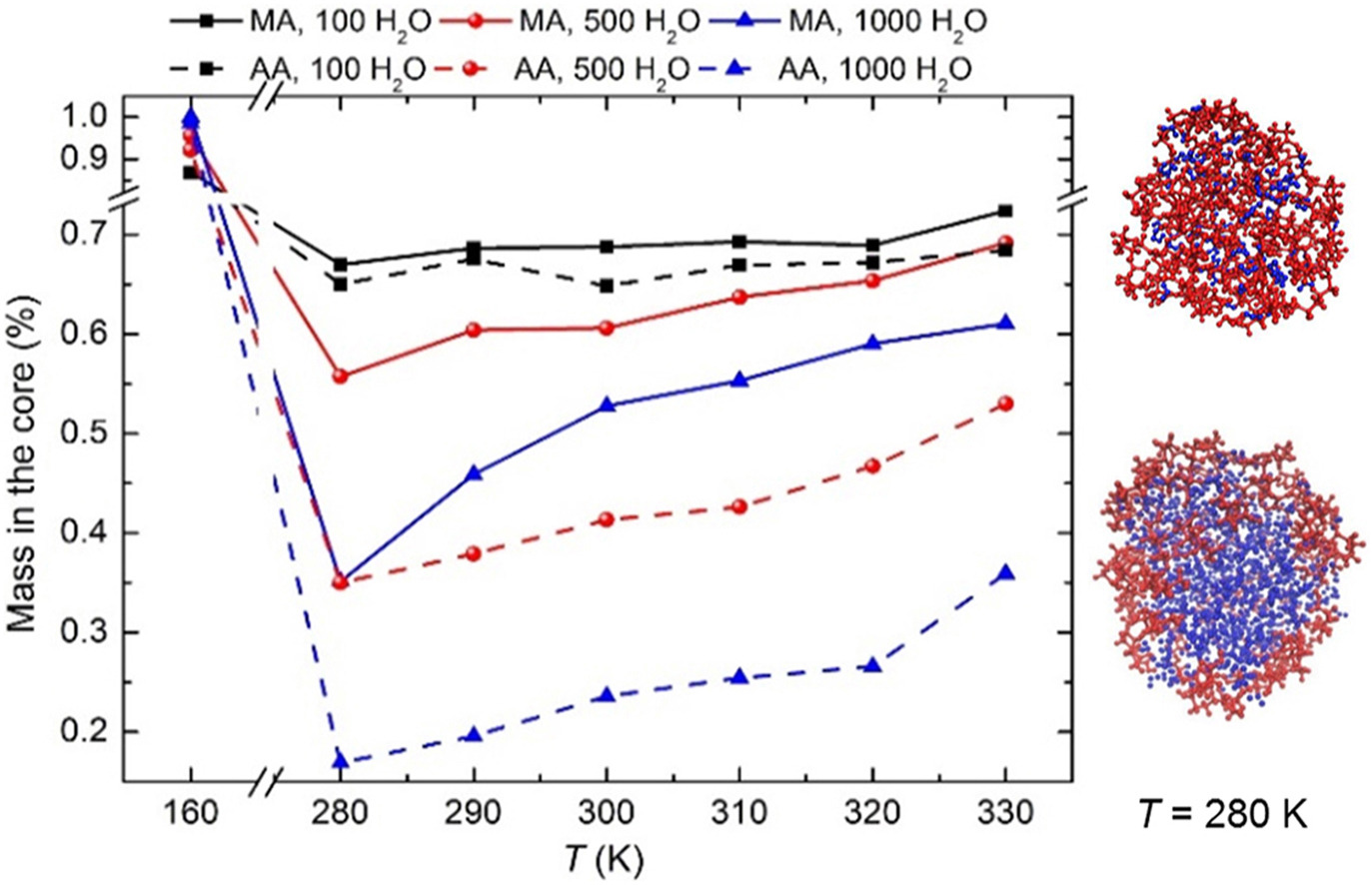
• Interaction between water and surfactant aerosol is studied using MD method.
• Various morphologies are observed for malonic acid (MA) (adipic acid (AA))-H2O particles.
• Surface propensity of MA and AA depends on temperature and water content.
• Effects of the MD results on hygroscopic properties are discussed.
The ubiquitous surfactant significantly influences the hygroscopic growth of atmospheric aerosol particles. However, knowledge on the morphology of surfactant particles after the adsorption of water is insufficient. In this study, the interaction between water and particles composed of surface active malonic acid (MA) or adipic acid (AA) are simulated based on the molecular dynamics method. The key point is the combined effect of temperature and water content on the structural properties of particles and the surface propensity of surfactants at the equilibrium state. Results show that demixed structure 1 with the adsorption of water clusters on acid grain, mixed structure and demixed structure 2 with acids coating on water droplet can be observed. With temperature increasing from 160 K to 330 K the surface propensity of MA and AA increases first and then weakens. Near the standard atmospheric temperature (280–330 K), the surface propensity of MA and AA increases with increasing water content and alkyl group, and its sensitivity to temperature and water content varies regularly. Moreover, all surfactants at the particle surface orient their hydrophobic groups toward the gas. These findings improve our insight into the surfactant partitioning and further assist in more accurate prediction of the particle hygroscopic growth.