- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
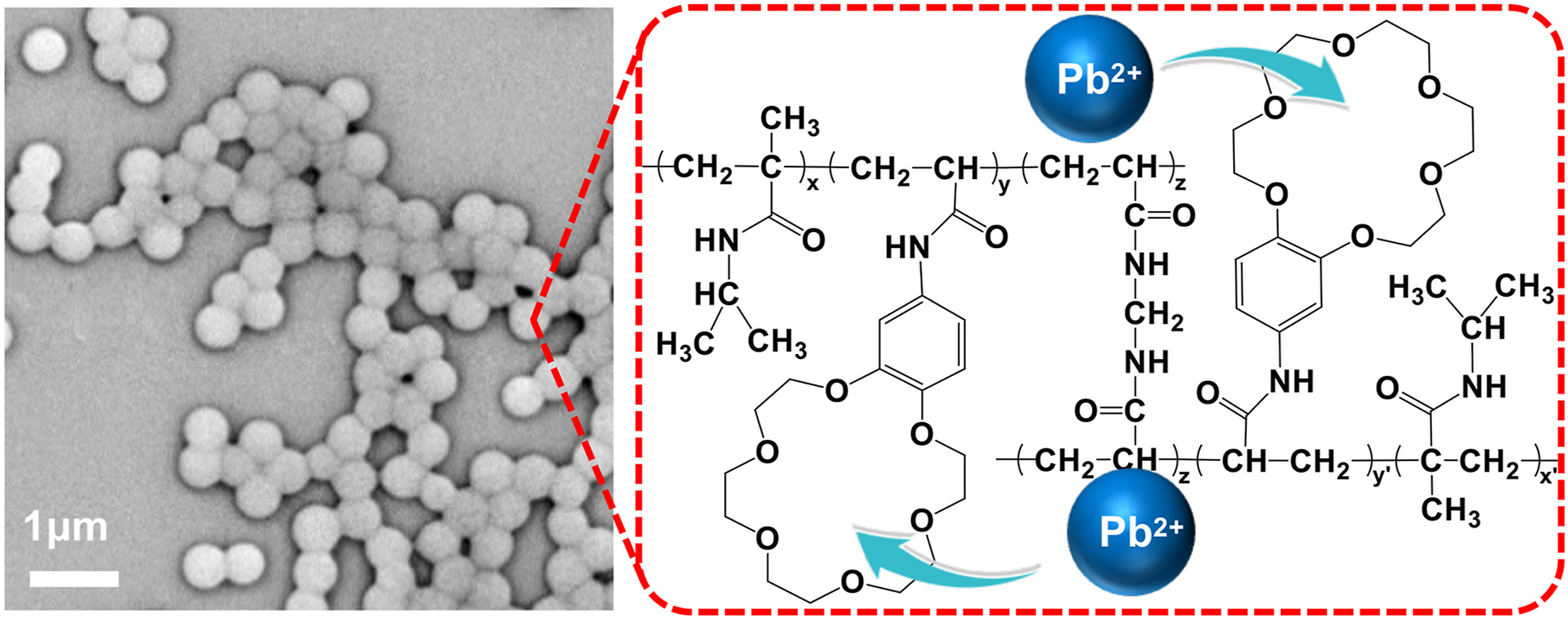
Fang Wang a, Zhuang Liu a b *, Rui Xie a b, Xiao-Jie Ju a b, Wei Wang a b, Da-Wei Pan a, Liang-Yin Chu a b *
• Poly(N-isopropylmethacrylamide-co-4-acrylamidobenzo-18-crown-6) (PNMB) microgels are developed.
• PNMB microgels exhibit expanded structures with low steric hindrance for adsorbing Pb2+.
• Maximum Pb2+ adsorption capacities of PNMB4 microgels are as high as 431.5 mg/g.
• Adsorption mechanism of PNMB microgels is Langmuir isotherm model.
Lead(II) (Pb2+) ions are toxic heavy metal ions that can accumulate in the human body through water and cause severe health problems, including neurotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, hematological toxicity and even genotoxicity effects. To remove Pb2+ selectively and effectively from aqueous solutions, we develop a novel type of PbPb2+-recognizable microgels with excellent adsorption capacity to Pb2+, which are fabricated from 4-acrylamidobenzo-18-crown-6 (B18C6Am) and N-isopropylmethacrylamide (NIPMAM) monomers by precipitation copolymerization method. The prepared poly(N-isopropylmethacrylamide-co-4-acrylamidobenzo-18-crown-6) (PNMB) microgels exhibit expanded structures, because the electron-donating methyl groups at α-carbon could descend the polarity of Cdouble bondO in the NIPMAM monomers and thus weaken the polymer segment···segment interactions. The expanded structures of PNMB microgels are beneficial for adsorption of Pb2+ due to the low steric hindrance in the polymeric networks. The Pb2+ adsorption isotherms of PNMB microgels are consistent with the Langmuir model for monolayer adsorption. The results indicate that the prepared Pb2+-recognizable PNMB microgels are highly promising for the selective removal of lead(II) ions from aqueous solutions.