- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
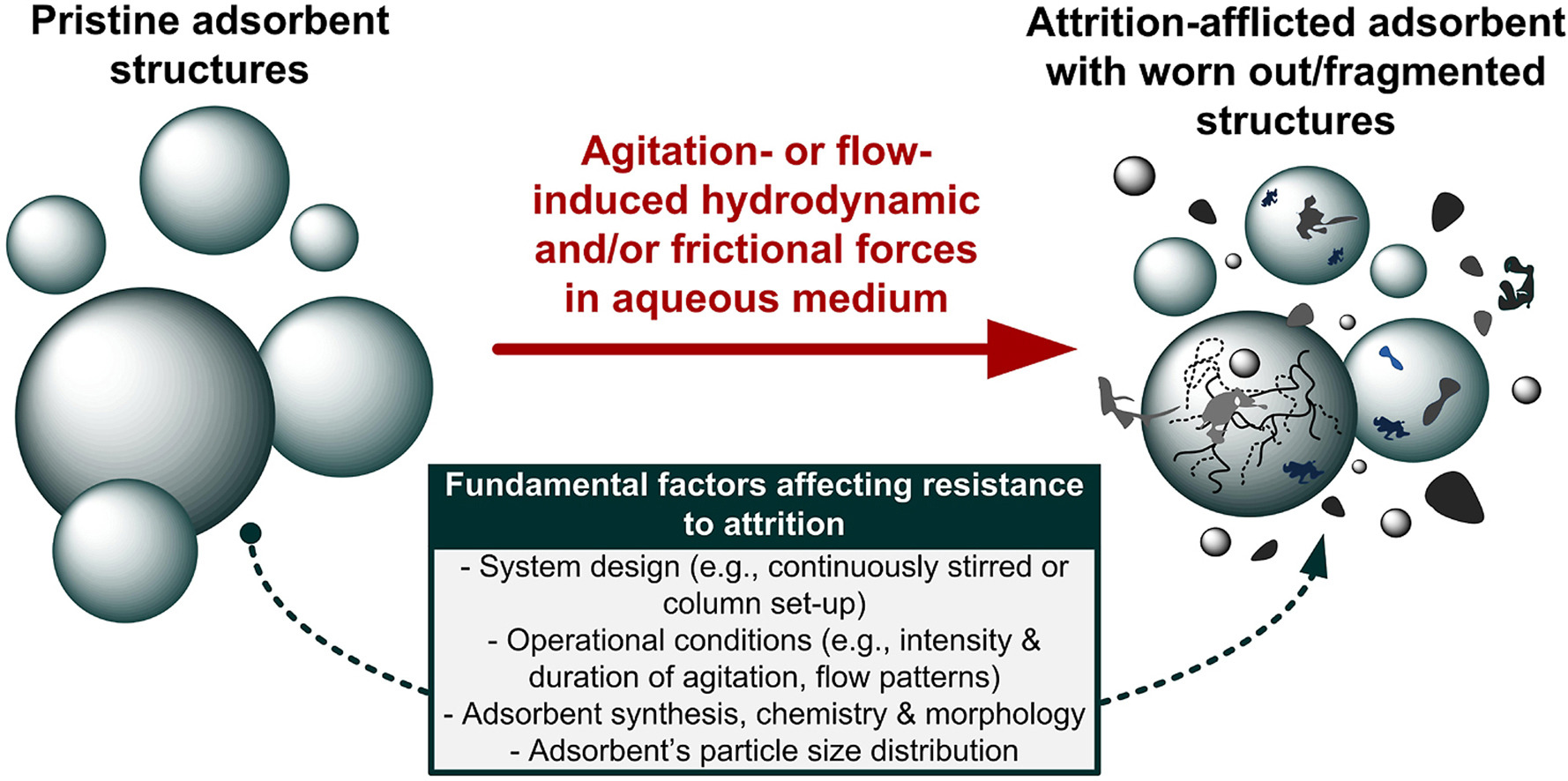
• Attrition resistance in aqueous-media adsorbents has been sporadically studied.
• The degree of attrition in an adsorbent depends on its synthesis and structure.
• Loss on attrition in adsorbents is mostly quantified by gravimetry-based methods.
• Analysis of attrition should be extended to large scale aqueous adsorption systems.
Attrition resistance in an adsorbent is one measure of its mechanical strength. It quantifies its ability to resist the impact of frictional forces generated in a milieu where hydrodynamic agitation exists. However, attrition resistance has been only sporadically examined in adsorbents used to remove aqueous adsorbates. Since attrition is relevant in aqueous adsorption process design, this review discusses the quantification of attrition resistance, variability in loss due to attrition across adsorbents, and the implications of attrition on adsorption systems. Finally, some key research opportunities that could be explored for a better understanding of attrition in real-scale water purification are presented. It is inferred that substantial research and development still needs to be accomplished to better understand the attrition resistance-adsorbent behavior within real-scale aqueous adsorption environments. The results can be harnessed to design and produce more robust, efficient and cost-effective adsorbents.