- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
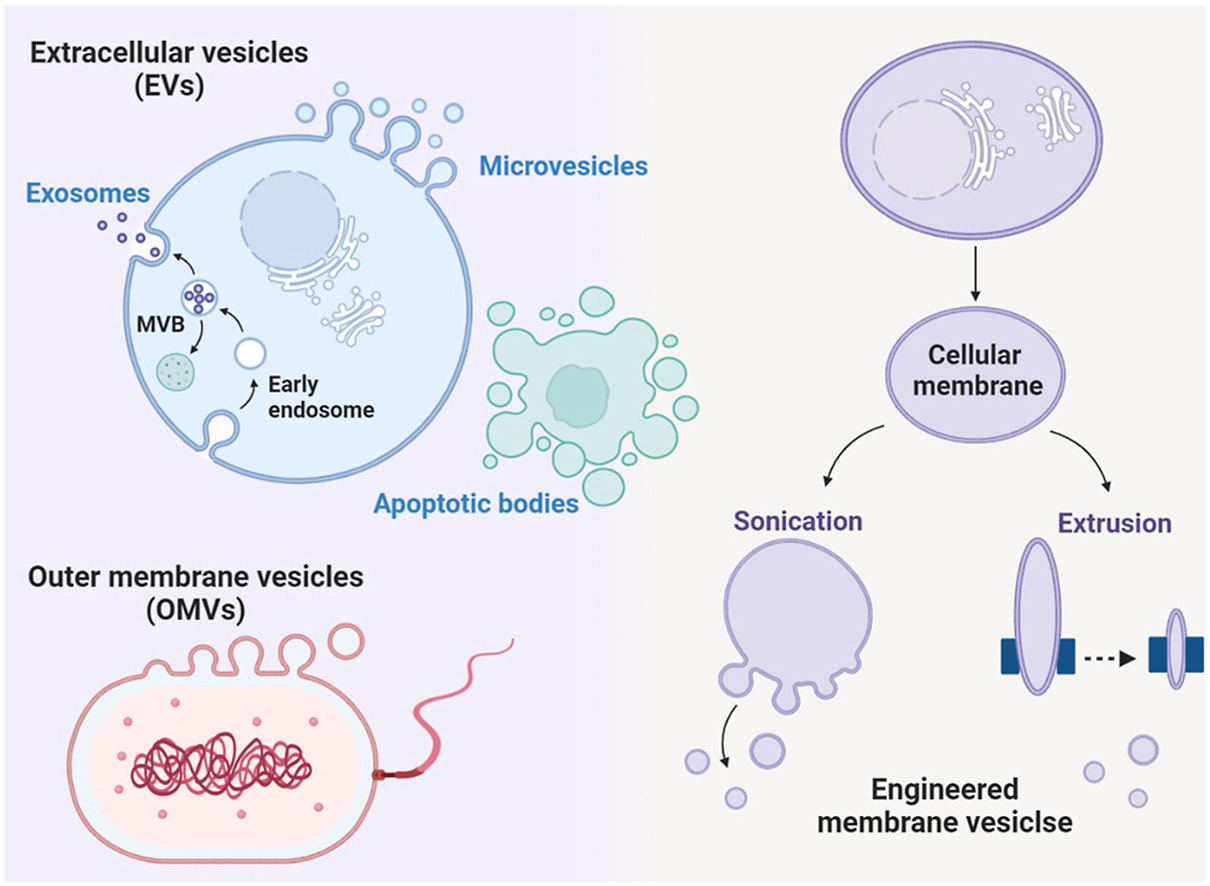
• Cytomembrane-based vesicles receive considerable attention in disease therapy.
• The ability to interact with biological molecules underlie cytomembrane-based therapy.
• Various modifications bestow cytomembrane-based vesicles with antibacterial effect.
• Techniques cross amplifies the effect of cytomembrane-based vesicles.
The emergence and re-emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, especially superbugs, are leading to complicated infections that are increasingly difficult to treat. Therefore, novel alternative antimicrobial therapies are urgently needed to reduce the morbidity and mortality caused by antibiotic resistance. The development of biomimetic-based therapy is expected to provide innovative means for addressing this challenging task. As a kind of novel biomaterial, cytomembrane-based vesicles (MVs) continue to receive considerable attention in antimicrobial therapy owing to their inherent biocompatibility, design flexibility, and remarkable ability to interact with biological molecules or the surrounding environment. These remarkable cell-like properties and their inherent interaction with pathogens, toxins, and the immune system underlie MVs-based functional protein therapy and targeted delivery to develop advanced therapeutic strategies against bacterial infection. This review provides a fundamental understanding of the characteristics and physiological functions of cytomembrane-based vesicles, focusing on their potential to combat bacterial infections, including detoxification, immune modulation, antibiotics delivery, and physical therapy. In addition, the future possibilities and remaining challenges for clinically implementing MVs in the field of antibacterial treatment are discussed.