- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
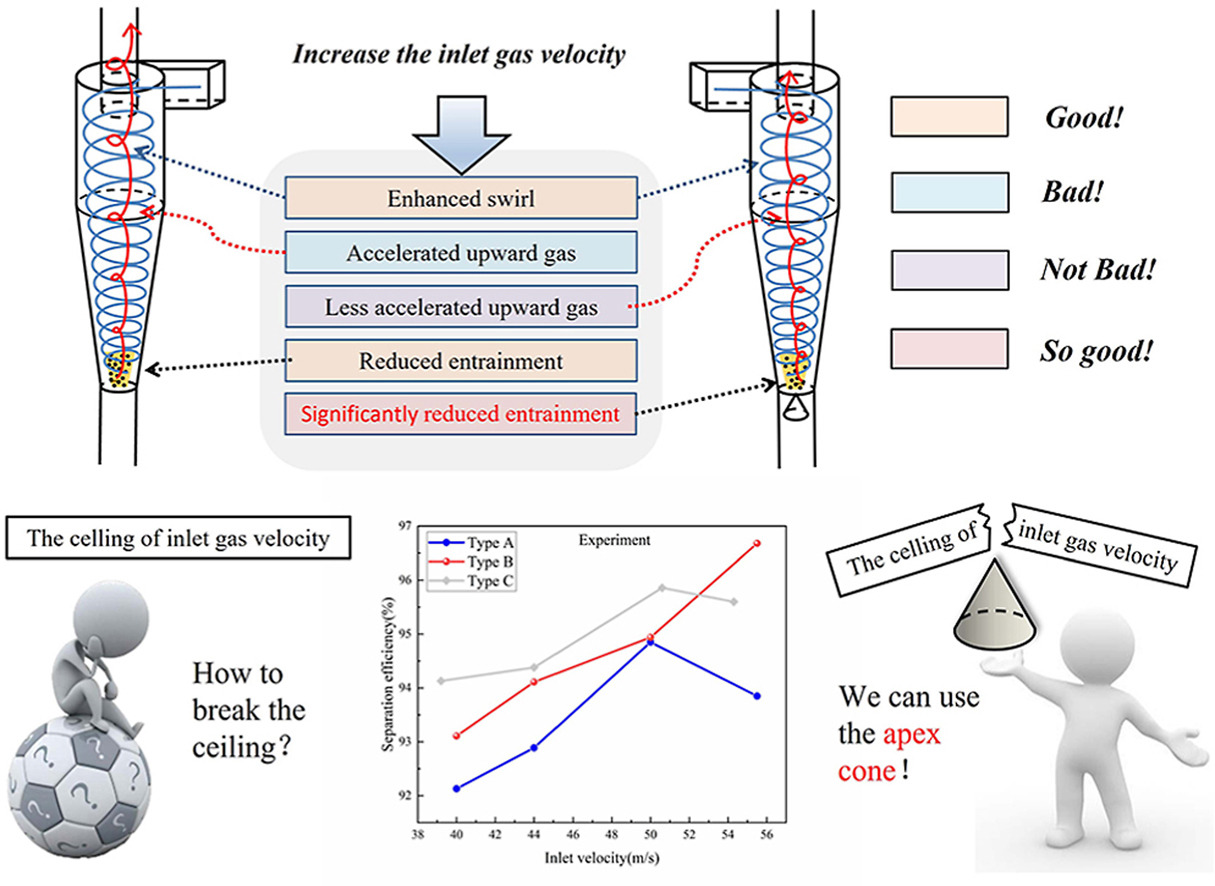
The maximum-efficiency inlet velocity (MEIV) is a ceiling of inlet gas velocity that defines separation efficiency during cyclone design and operation. Experiment and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation exhibited that an apex cone at the dust outlet can break the ceiling and improve the separation efficiency. The phenomenon is closely related to the effect of excessive high inlet gas velocity on the back-mixing escape of fine particles, which is the final result of back mixing, entrainment by the rapid upward airflow, and secondary separation of the inner vortex. In the center of the inner vortex, the airflow rotates slowly and moves rapidly upward. This elevator type of airflow delivers re-entrained particles to the vortex finder. A higher inlet gas velocity accelerates the elevator, causing more entrained particles to escape. This explains the decrease in efficiency at an excessively high inlet gas velocity. When an apex cone is installed at the dust outlet, the back-mixing is significantly weakened because the vortex core is bounded to the center of separator, while the transport effect of rapid upward airflow is weakened by the decrease in axial velocity in the center. Therefore, particle escape is weakened even at excessive high inlet gas velocities. Instead, the centrifugal effect is enhanced because of increased tangential velocity of the gas and particles. Consequently, the ceiling of inlet gas velocity is broken.