- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
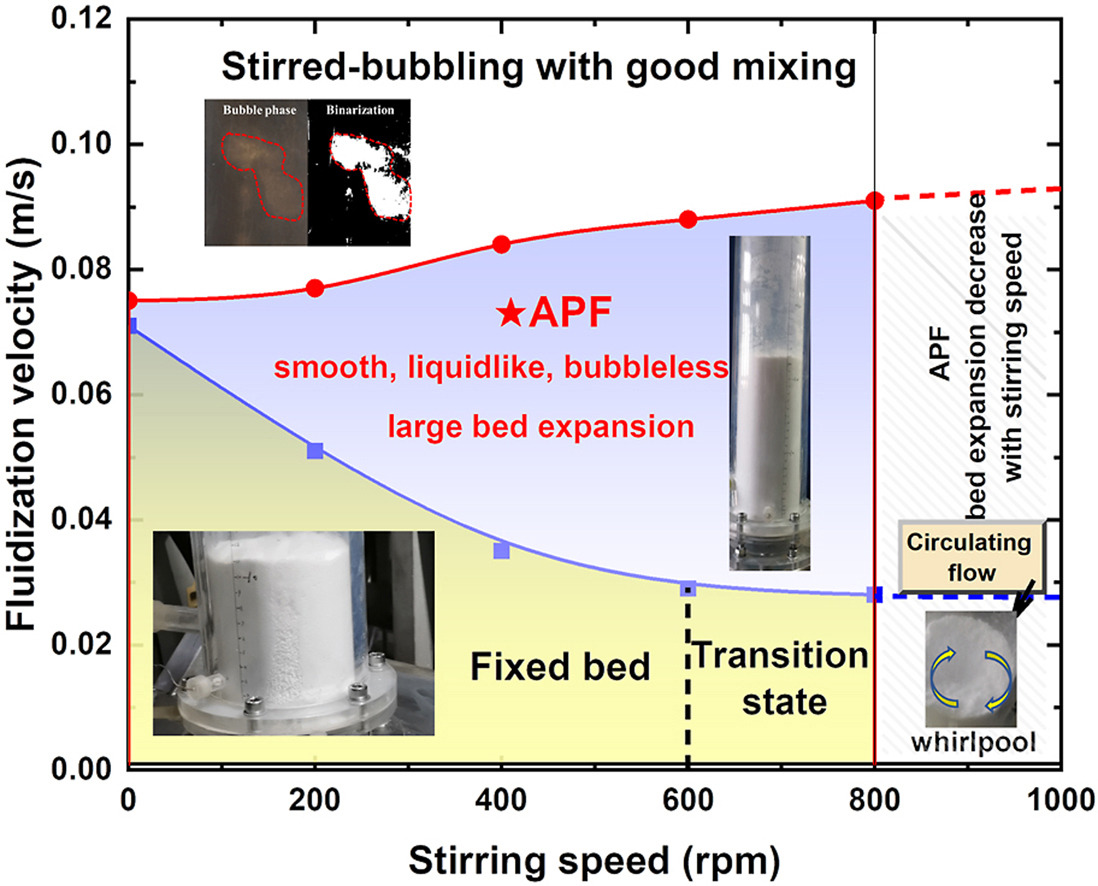
• A high-speed stirring fluidized bed is designed to improve the fluidization of cohesive powders.
• The powders are well dispersed in the regime of agglomerate particulate fluidization.
• Transitions of different fluidization regimes are depicted comprehensively.
• The stirring applied enlarges the operational range of agglomerate particulate fluidization.
• The agglomerate sizes tend to the original particle size with high stirring speed.
The effects of superficial gas velocity and mechanical stirring speed on the precise regulation of flow regimes for cohesive SiO2 powders (mean diameter is 16 μm) were experimentally investigated in a stirring-assisted fluidized bed. The results showed that compared with the agglomerates formed in the non-assisted fluidization of cohesive SiO2 powders, the introduction of mechanical stirring could effectively reduce the size of agglomerates and well disperse the agglomerates during fluidization. The best regulation range of agglomerate particulate fluidization can be achieved at 600 rpm when agglomerate sizes were reduced to below 200 μm. Further investigation based on the operational phase diagram revealed that transformations of flow regimes were dominated by both stirring speed and gas velocity. The stirring applied enlarges the operational range of agglomerate particulate fluidization (APF) with a delayed onset of bubbling for cohesive particles. However, the exorbitant speed increases the collision velocity and contact area between small agglomerates, which results in the formation of unstable agglomerates and the whirlpool of powder.