- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
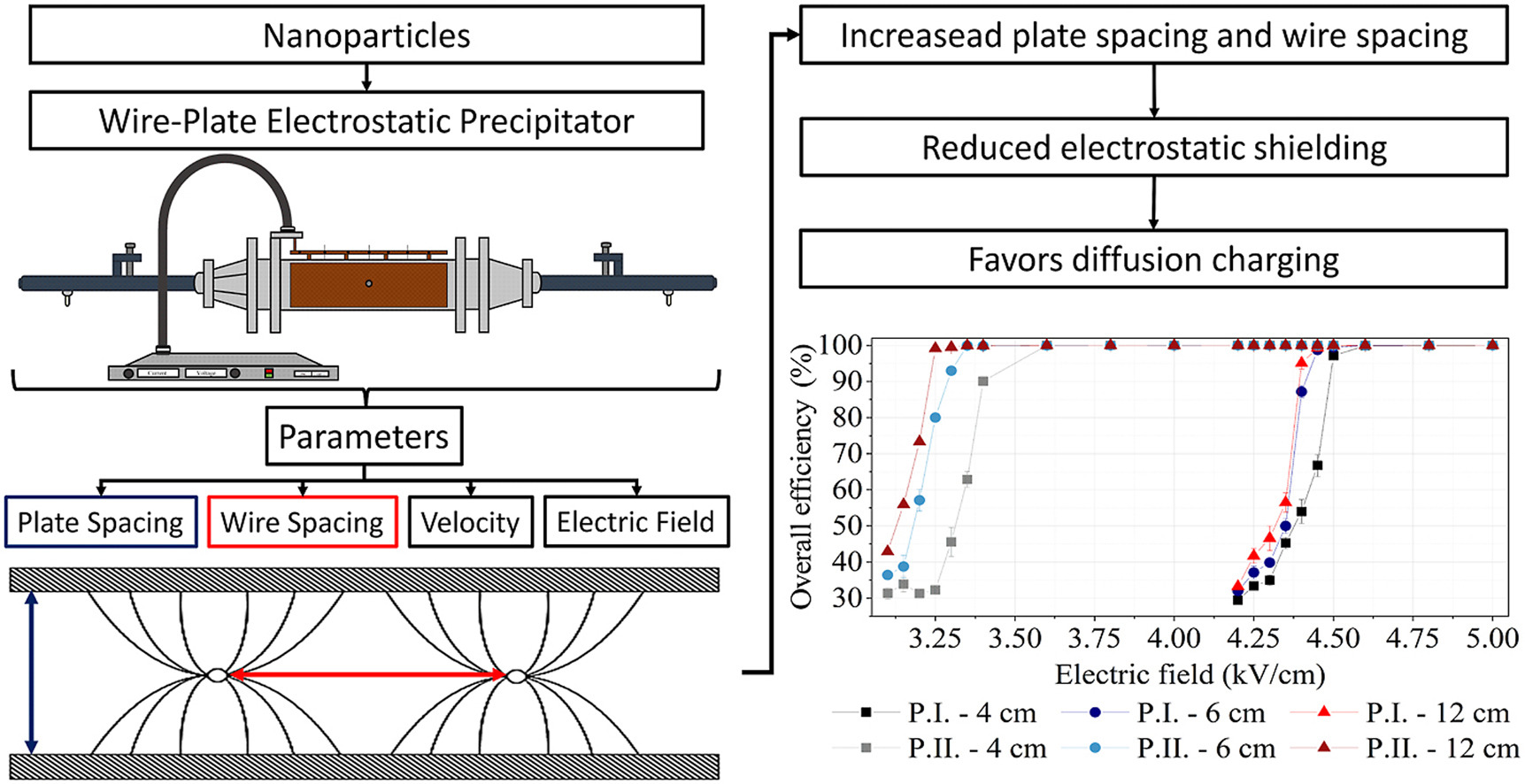
• Evaluation of ESP geometric parameters in the efficiency of nanoparticle collection.
• A greater wire spacing or plate spacing promotes greater collection efficiency of nanoparticles.
• The plate and wire spacing affects the electrostatic shielding and diffusion charging phenomena.
• Electrical current increased with increasing wire spacing due to lower electrostatic shielding.
• A greater plate spacing reduces the electrostatic shielding and contributed to greater charging.
Electrostatic precipitation is a process widely used as gas cleaning device, to removal particles from gas flows. However, in a conventional and well-sized precipitator, the collection efficiency decreases for ultrafine particles, making it difficult to employ this equipment for controlling nanoparticle pollution. This paper investigates the influence of plate spacing (4 and 6.5 cm) and wire spacing (4, 6, and 12 cm) on the electric current and nanoparticle collection efficiency, considering the effect of diffusion charging and electrostatic shielding. Two laboratory-scale dry wire-plate electrostatic precipitators with different plate spacings were tested for the collection of nanoparticles (6.15–241.4 nm) at three air velocities (1.9, 2.9, and 3.9 cm/s). The results demonstrated the effectiveness of the equipment in removing nanoparticles (99.9%) under the highest electric fields. Higher values of the wire spacing led to increases in the current and the collection efficiency. This was associated with reduced electrostatic shielding, which is more evident in smaller ducts with a higher density of field lines. It is expected that the findings should improve knowledge on electrostatic precipitation of nanoparticles, enabling optimization of collection efficiency by considering the effects of geometric parameters.