- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
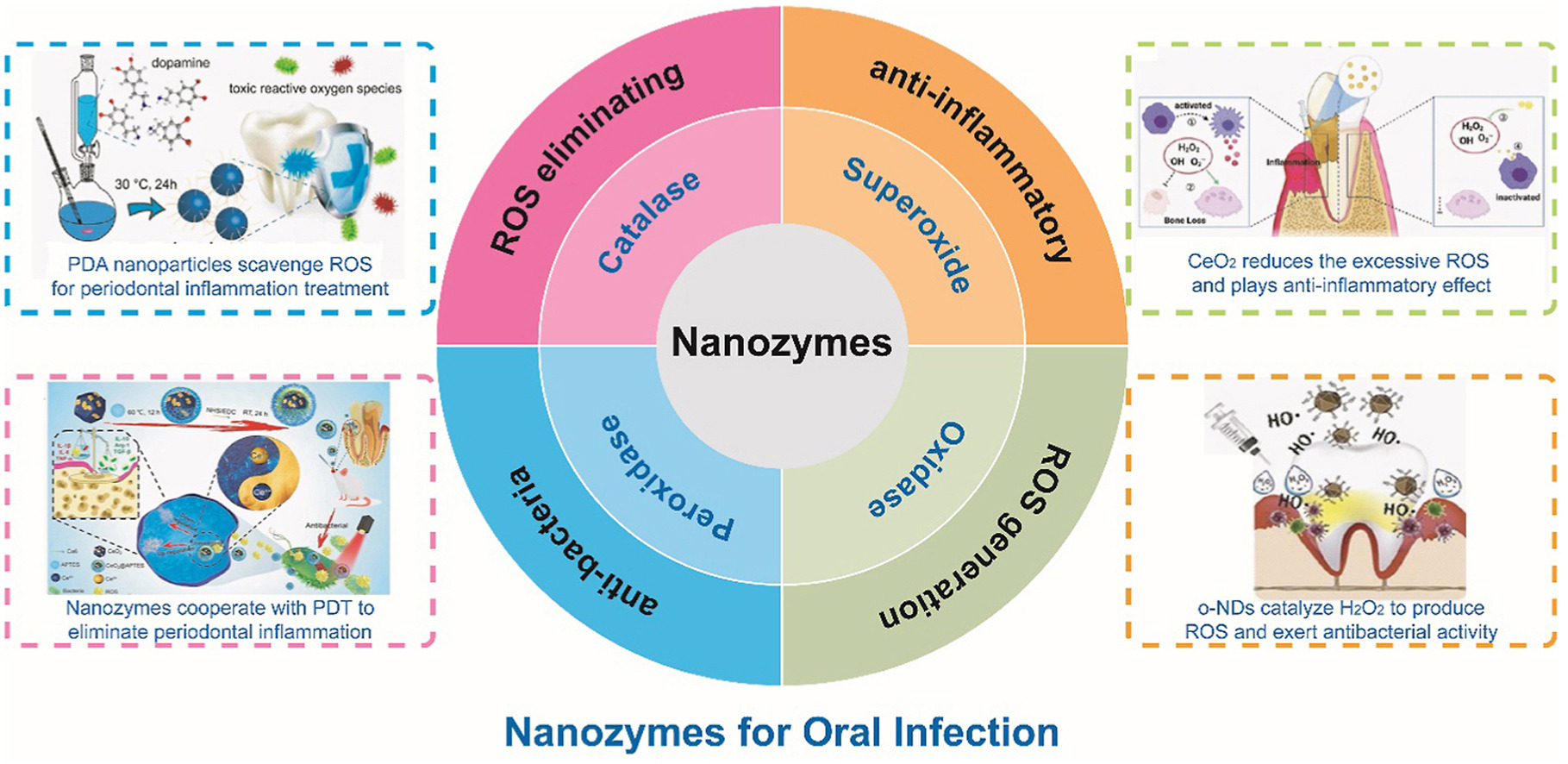
• Nanozymes have attracted admirable attention in various biomedical fields.
• Nanozymes have been well developed as efficient therapeutic agents in oral infection.
• Nanozymes reveals great potential for more oral diseases in further clinical setting.
As a category of nanomaterials with excellent catalytic efficiency, great substrate specificity, and high recovery efficiency, nanozymes have attracted increasing attention in various biomedical applications. Currently, numbers of nanozyme-assisted strategies have been well developed for the theranostics of various diseases by taking advantages of their multienzyme-like characteristics, low cost, and high stability. As the most prevalent oral diseases, oral infection poses a global hazard to human health, and current therapeutic options are insufficient to resolve all the clinical issues. Based on their admirable activity, nanozymes can be frequently employed in the identification and treatment of various oral infectious disorders. Herein, we provide a brief review focused on the classification of nanozymes, analyses of nanozyme-based antibacterial mechanism, research progress in oral bacterial control, and representative studies of nanozyme-assisted oral inflammatory management. Moreover, major challenges and potential opportunities regarding the use of nanozymes in oral infectious diseases are also highlighted and discussed. This review not only summarizes the recent studies of nanozymes in oral infection but also promotes the further development of enzyme-mimetic strategies towards various oral diseases.