- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
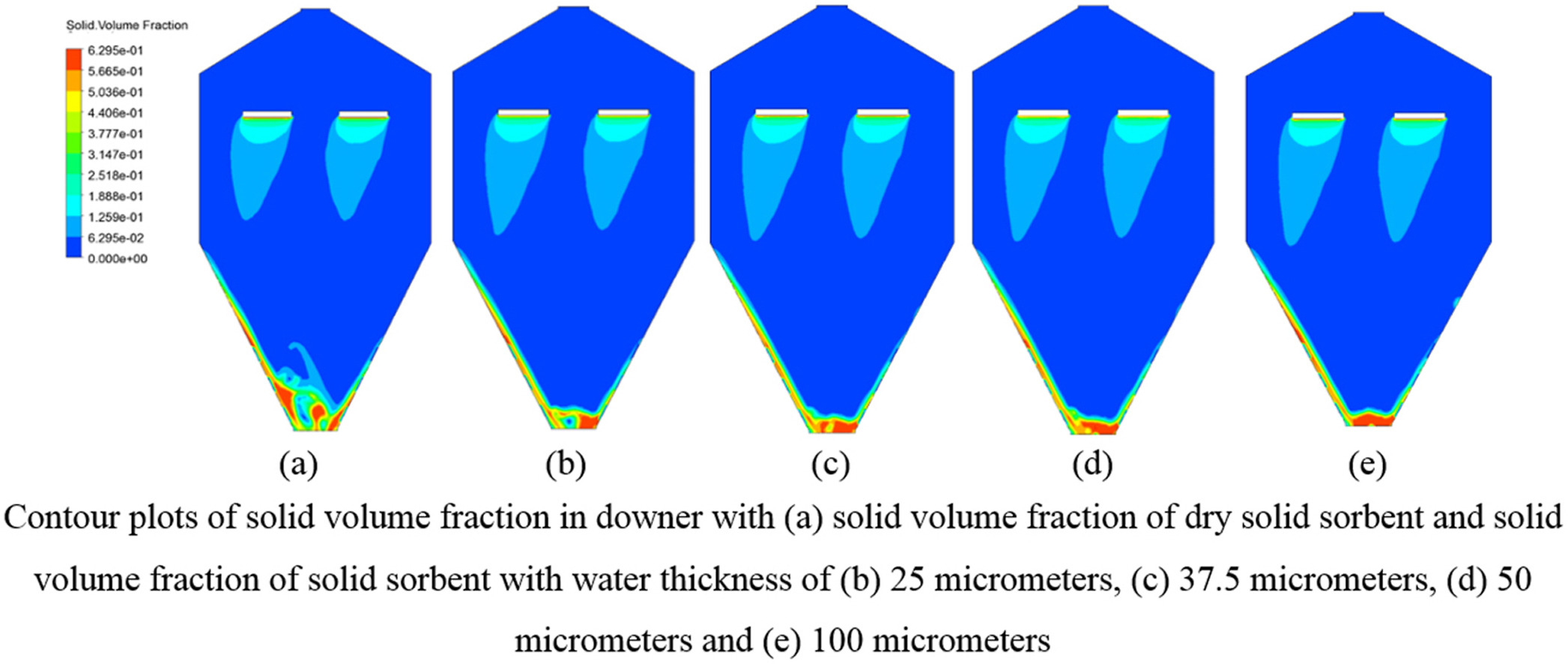
• CO2 desorption of K2CO3/γ-Al2O3 in a wet fluidized bed was investigated using CFD.
• Effects of water thickness and dry restitution coefficient were modeled.
• Increasing water thickness obstructed the solid movement in the reactor downer.
• Increase in the dry restitution coefficient decreased the CO2 desorption.
• Wet operating conditions gave different desorption behavior with the dry ones.
Since the carbon dioxide (CO2) capture using solid sorbent is a reversible reaction, the solid sorbent can be regenerated by the desorption process. Therefore, the desorption process is one of the key important processes for the CO2 capture system. Traditionally, most of the literature studies focus on the desorption of solid sorbent under an N2 atmosphere. However, the desorption process of the solid sorbent is inappropriate in the real system because the system will need another process to separate CO2 and nitrogen (N2) after the desorption process. This study focused on the CO2 desorption of potassium carbonate supported on gamma-alumina (K2CO3/γ-Al2O3) in a wet fluidized bed under a steam atmosphere by using the multiphase computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation. The effects of water thickness and dry restitution coefficient on CO2 desorption rate were investigated to provide a realistic particle collision behavior and to explore their effects on CO2 desorption phenomena. Moreover, the effect of steam velocity on the hydrodynamic behaviors of fluidization which on CO2 desorption rate was studied. The simulated results demonstrated that all the parameters, water thickness, dry restitution coefficient, and steam velocity had significantly affected system hydrodynamics and CO2 desorption rate in the wet fluidization desorption process. Furthermore, the effect of desorption temperature on CO2 desorption rate was evaluated for finding the appropriate temperature for CO2 desorption process of K2CO3/γ-Al2O3. The results showed that the appropriate desorption temperature for CO2 desorption under steam atmosphere was the temperature over 150 °C.