- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
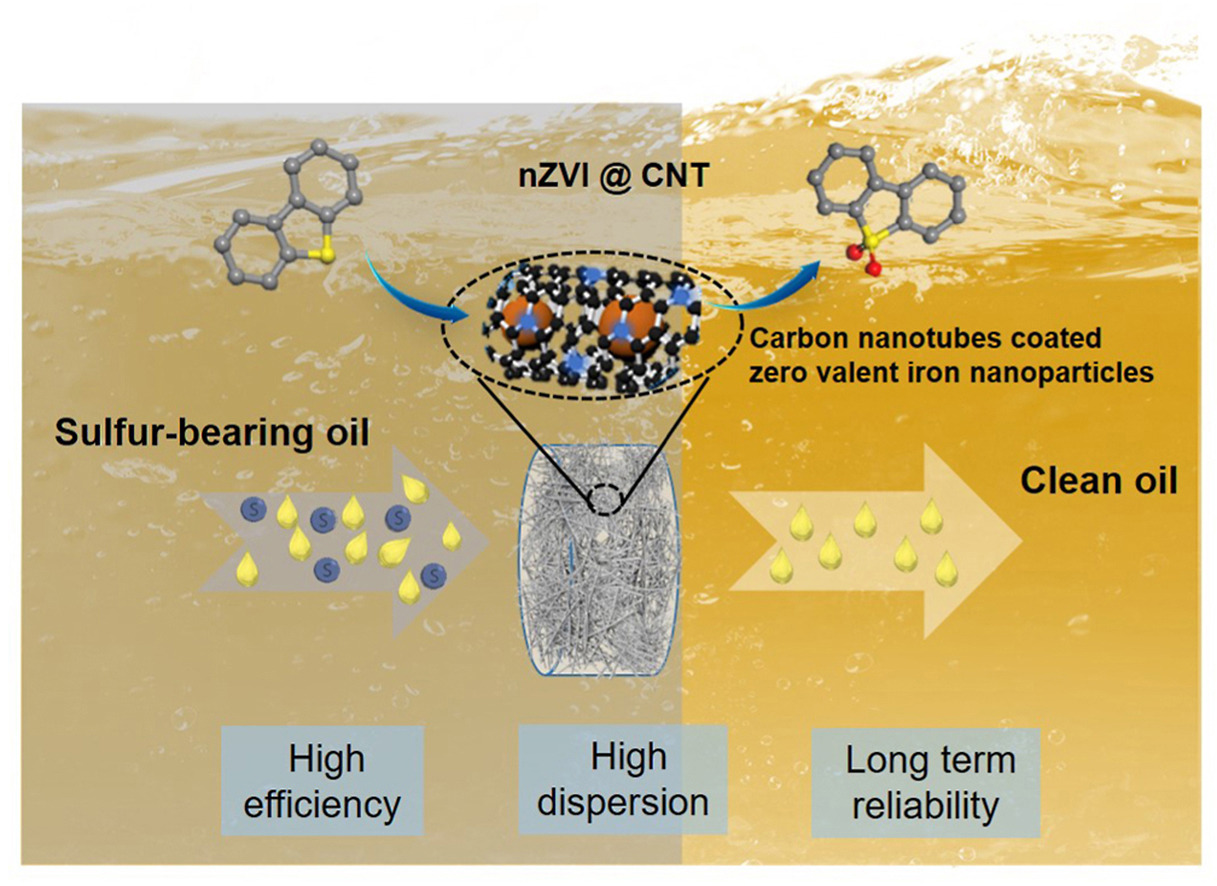
• Carbon nanotube as structure enhancer for iron led to higher stability of nano zero valent iron (nZVI).
• Electron-rich N-doped carbon enhanced the dispersion of nZVI by interfacial charge transfer.
• Two-dimensional tube channel promoted the diffusion and transfer of reactants and electrons.
• Highly active free radicals from H2O2 improved the oxidation desulfurization activity of nZVI.
Great efforts have been made to remove sulfur from fossil fuels to protect the environment. We proposed synthesis of high efficiency oxidation desulfurization (ODS) catalysts by encapsulating nano zero valent iron (nZVI) in self-catalyzed carbon nanotubes. The synthetic strategy features facile hydrothermal and pyrolysis process. The specific surface area, pore structure, and microstructure of the catalysts were characterized by series techniques, and the catalytic ability was evaluated by the reduction of sulfur after oxidation and reflux-extraction. The optimized nZVI@CNT catalyst exhibits outstanding catalytic performance (within 120 min, the oxidative removal rate of DBT reached 96%) and enhanced stability (a 80% retention of initial performance after six cycles.), revealing the effective optimization and modulation between carbon nanotubes and iron particles. This excellent ODS activity originated from the defects of N-doped nanotubes as well as excellent particle dispersion and material transport capacity, which excites highly active free radicals with the assistance of H2O2. In addition, the unique two-dimensional tube channel and mesoporous structure promoted the diffusion and transfer of reactants and electrons, leading to high density of active sites. The different experimental conditions confirmed that the material is a bifunctional catalyst integrating adsorption and catalysis. This work provides an creative ideas for the rational design and synthesis of advanced ODS catalysts for fuel oil.