- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
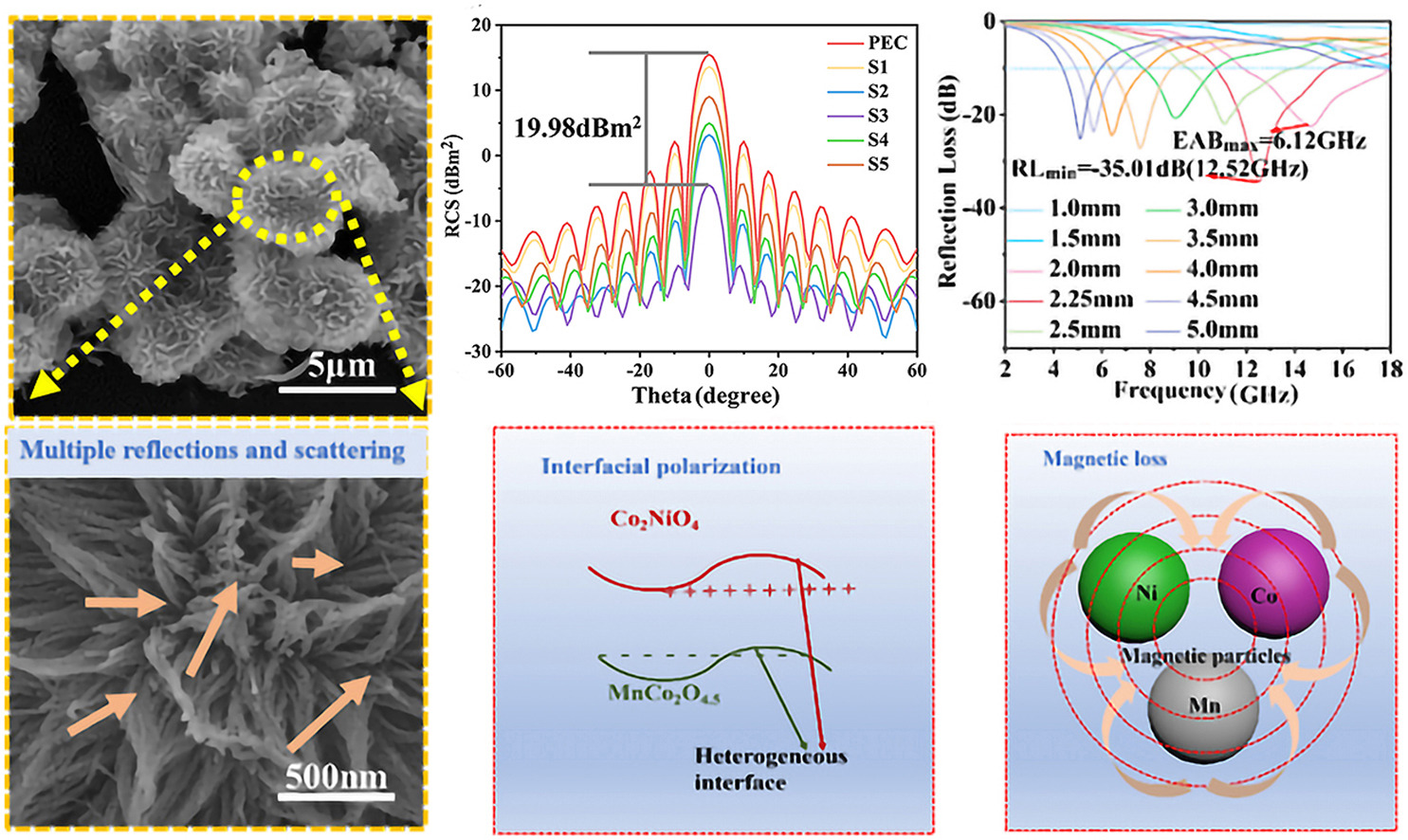
• Co2NiO4@MnCo2O4.5nanoparticles were successfully constructed with multiple magneto-electric loss mechanisms.
• MnCo2O4.5 produce more vacancies and contribute to the enhancement of electrical conductivity.
• Nanoneedle arrays provide numerous hetero-interfaces and high specific surface areas for Co2NiO4@MnCo2O4.5 composites.
• Co2NiO4@MnCo2O4.5 composites showed a RLmin of -30.01 dB and a superior EAB of 6.12 GHz.
• Maximum reduction of RCS at vertical incidence reaches 19.98 dBm2, exhibiting outstanding radar attenuation properties.
Nanocomposites with heterogeneous structures and magneto-electric synergistic losses have broad prospects for improving electromagnetic wave (EMW) absorption performance. In this study, we synthesized Co2NiO4@MnCo2O4.5 nanoparticles with abundant hetero-interfaces and multiple magneto-electric loss mechanisms by a facile hydrothermal method. The excess 0.5 oxygen atoms in MnCo2O4.5 produce more vacancies and contribute to the enhancement of electrical conductivity. Sequential nanoneedle clusters facilitate multiple reflections and absorption of EMW in the materials, which are accompanied by an abundance of heterogeneous interfaces to improve the dielectric loss. The Co2NiO4@MnCo2O4.5 composites showed a minimum reflection loss (RLmin) of −30.01 dB and a superior effective absorption bandwidth (EAB) of 6.12 GHz (11.88 GHz–18 GHz) at a thickness of 2.00 mm. Computer Simulation Technology (CST) revealed that the obtained particles show very low radar cross-section (RCS) values and almost full coverage angles. The maximum reduction of RCS at vertical incidence reaches 19.98 dB m2. The Co2NiO4@MnCo2O4.5 nanoparticles exhibit outstanding radar attenuation properties, which can effectively inhibit the reflection and scattering of EMW. Therefore, the prepared Co2NiO4@MnCo2O4.5 absorbers have great application potential in the field of EMW absorption.