- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• A new lithiation boundary is proposed by utilizing capacity below 0 V of hard carbons (HCs).
• The boundary provides a nearly twice capacity improvement.
• The lithium storage mechanism below 0 V of HCs is investigated.
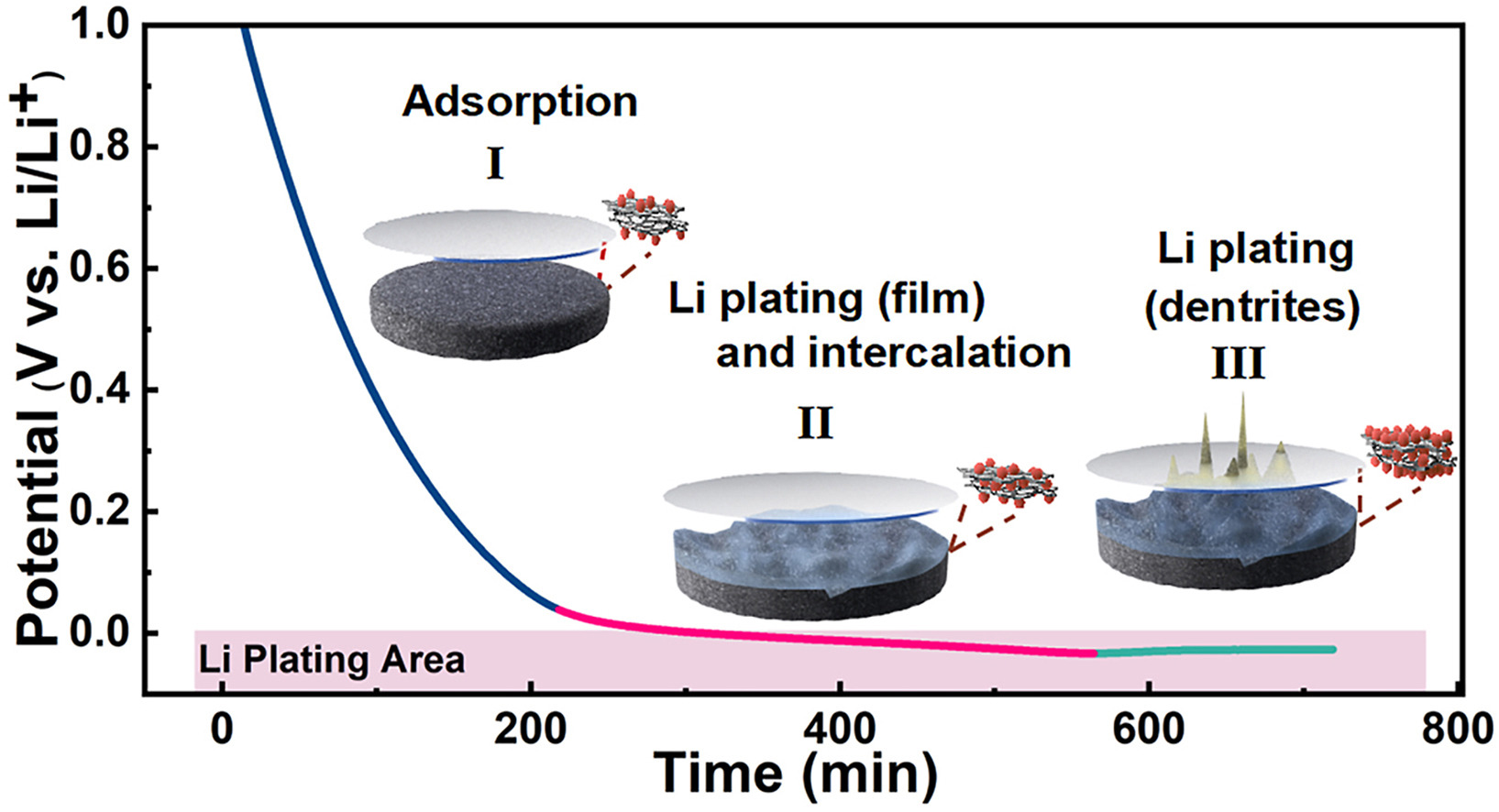
Compared with conventional graphite anode, hard carbons have the potential to make reversible lithium storage below 0 V accessible due to the formation of dendrites is slow. However, under certain conditions of high currents and lithiation depths, the irreversible plated lithium occurs and then results in the capacity losses. Herein, we systematically explore the true reversibility of hard carbon anodes below 0 V. We identify the lithiation boundary parameters that control the reversible capacity of hard carbon anodes. When the boundary capacity is controlled below 400 mAh g−1 with current density below 50 mA g−1, no lithium dendrites are observed during the lithiation process. Compared with the discharge cut-off voltage to 0 V, this boundary provides a nearly twice reversible capacity with the capacity retention of 80% after 172 cycles. The results of characterization and finite element model reveal that the large reversible capacity below 0 V of hard carbon anodes is mainly benefited from the dual effect of lithium intercalation and reversible lithium film. After the lithium intercalation, the over-lithiation induces the quick growth of lithium dendrites, worsening the electrochemical irreversibility. This work enables insights of the potentially low-voltage performance of hard carbons in lithium-ion batteries.