- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
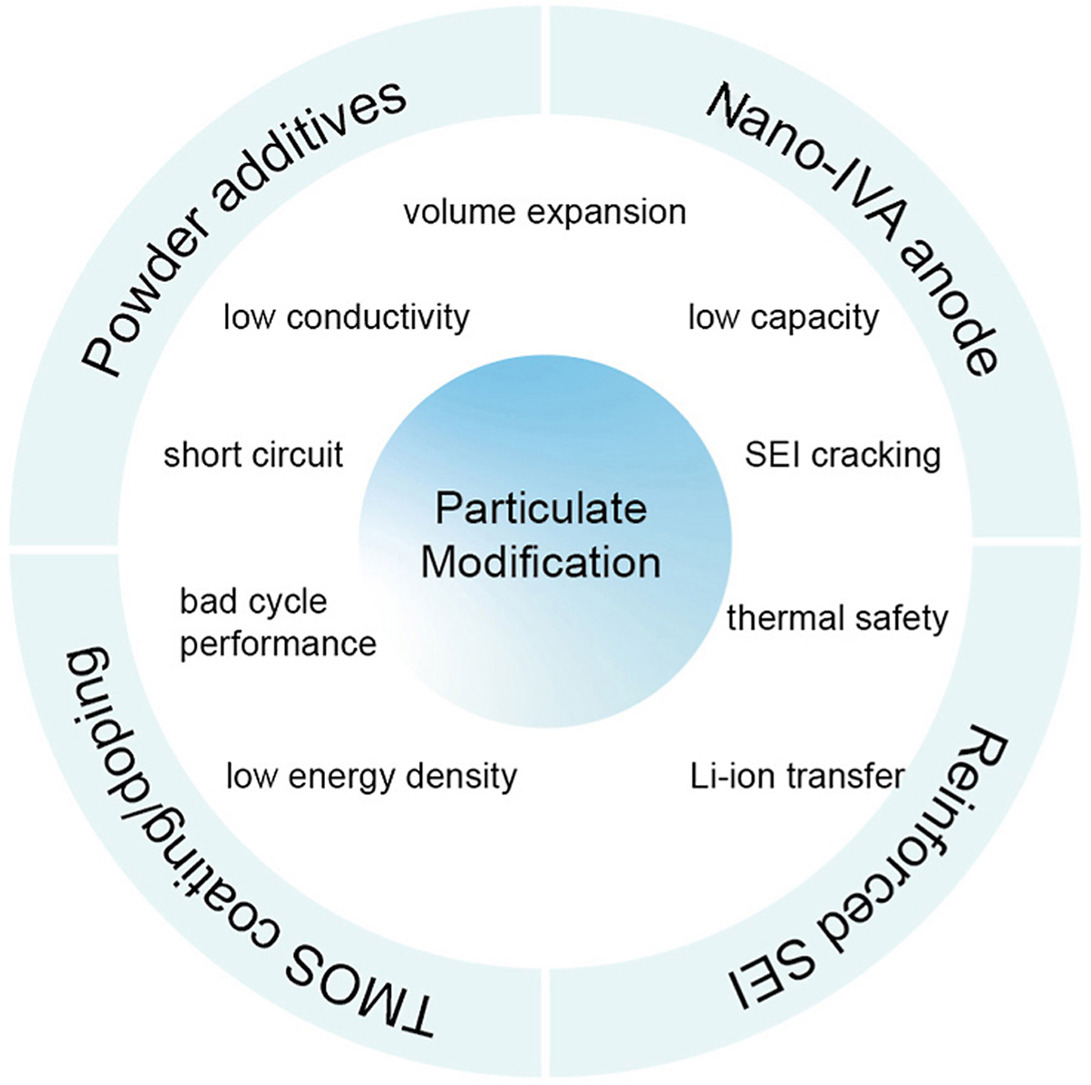
• Particulate modification of lithium-ion battery anode materials and electrolyte are reviewed.
• Challenges occurred in anode and electrolyte are discussed.
• Particulate modification for group IVA anode materials and electrolytes are introduced.
• Research progress on transition metal oxide nanoparticles into the anode are introduced.
• Research progresses on enhancement of solid electrolyte interface are introduced.
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) are considered a rechargeable and commercial energy storage device for electronic equipment such as smartphone and electric vehicles. Despite the prospective future of LIBs, unsatisfied electrochemical properties like reversible capacity, cycle ability and coulombic efficiency still hinder their development. High volume expansion rate, uncontrolled Li dendrite growth and unsatisfied solid electrolyte interphase also occur when LIBs are applied in long-time usage. Numerous modification methods such as exploring high-capacity anode/cathode materials, constructing artificial solid electrolyte interphase and improved conductive binders can be adopted to enhance the performances. Among them, particulate modification for LIBs anode and electrolytes is receiving tremendous attraction in the recent work. The method is composed of changing the morphology and particle size of the active materials, also introduce nano-size additives to the main structure. This review emphasizes on introducing and discussing the modification in following aspects: particulate modification on carbon group IVA element anodes, introduction of additives like transition metal oxide nanoparticles into anode and electrolyte materials, dissipate the influence of Li dendrite growth and ameliorate the performances of solid electrolyte interface. This review hopes to be denoted for the future development of LIBs with the comprehensive understanding on the particulate modification.