- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
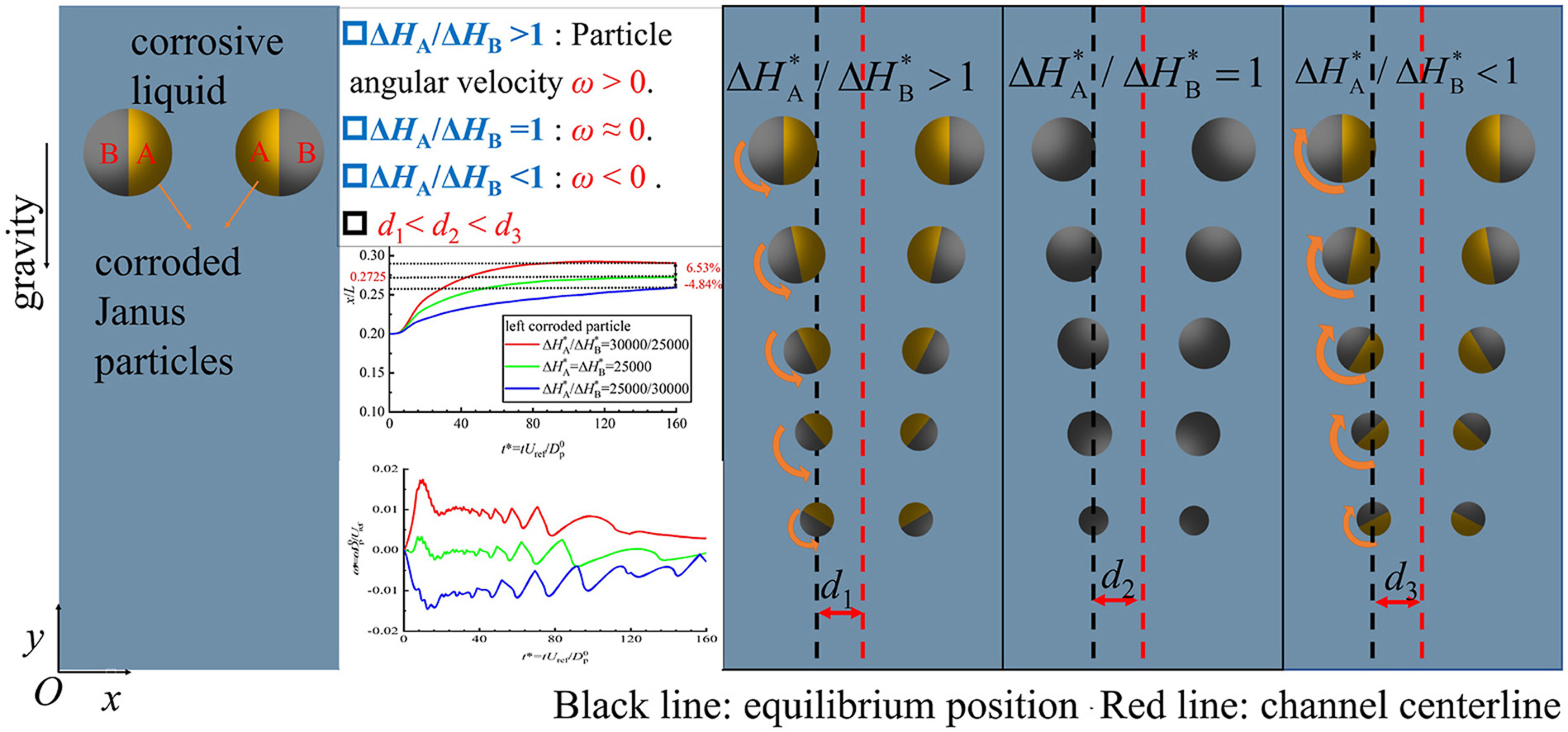
• Corroded Janus particle settling process is investigated by IB-LBM.
• Chemical reaction heat ratio and particle number effects are revealed.
• Janus particle mass reduction, position and velocity are investigated.
• Janus particle position deviates from the uniform particle equilibrium position.
• Reaction rate affects concentration and temperature inhomogeneity.
Janus particle is a research hotspot due to its novelty and settlement in acid liquid during wastewater treatment. Heat and mass transfer mechanisms of Janus particle sedimentation considering corrosion are numerically investigated based on immersed boundary lattice Boltzmann method. Chemical reaction heat ratio, Damkohler number, Peclet number, and particle number effects on temperature field, concentration field, Janus particle mass reduction, position, and velocity are investigated. The uniform particle has an equilibrium position of about 1/4 times the channel width for two corroded uniform particle settlement processes. The Janus particle horizontal position deviates from the uniform particle equilibrium position due to the force caused by nonuniform buoyancy and particle rotation. When the chemical reaction heat ratio is more than 1, the Janus particle horizontal position is closer to the channel centerline and has a positive deviation. However, the converse trend happens when the chemical reaction heat ratio is less than 1, and the Janus particle horizontal position has a negative deviation. The Janus particle horizontal position deviation magnitude increases with increasing Damkohler number and decreasing Peclet number. The horizontal position deviation phenomenon exists for the single corroded Janus particle and two corroded Janus particle settlement processes.