- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
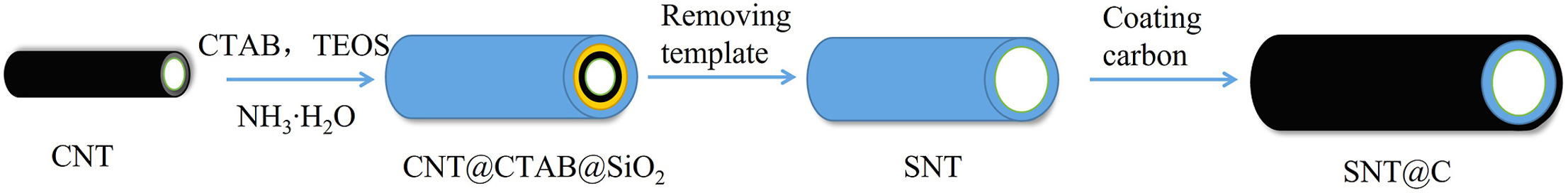
• Silica nanotubes were prepared as lithium ion battery anode materials using carbon nanotubes as templates.
• Citric acid was used as carbon source to improve electronic conductivity and cycle stability of silica nanotubes.
• The method is applicable to large-scale production of silica anode materials for lithium-ion batteries.
Silica-based anode material is the most concerned material at present, which has the advantages of good cycle stability, high theoretical specific capacity and abundant reserves. However, silica suffers from inherent low conductivity, severe volume expansion effect and low initial coulombic efficiency, which limits its application in lithium-ion batteries. Nanotubes structure can mitigate the volume expansion during lithiation/delithiation. In this article, silica nanotubes (SNTs) were prepared using carbon nanotubes (CNTs) as a template, and then the uniform carbon layer was coated on their surface by carbonization of citric acid. The hollow structure of nanotubes provides more sites for the insertion of Li+ during lithiation and additional channels for Li+ migration in the cycles, which improves the electrochemical performance. Conductivity can be enhanced by coating carbon layer. The specific capacity of the composite material is about 650 mAh g−1 at 0.1 A g−1 after 100 cycles. With a specific capacity of 400 mAh g−1 even at 1 A g−1 after 100 cycles. The silica-based material is a competitive anode material for lithium-ion batteries.