- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
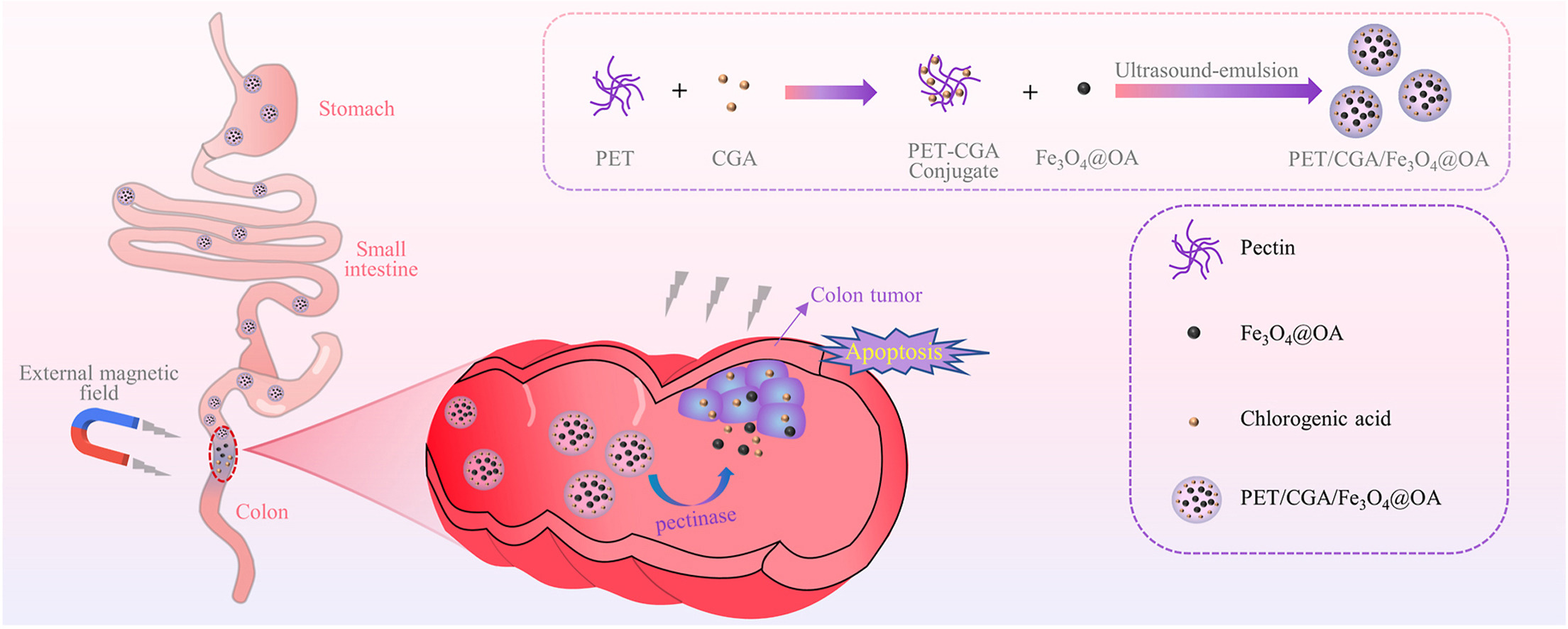
• Preparation of magnetically driven pectin particles by ultrasonic emulsification.
• Construction of a pectin-based delivery vector for oral colon cancer therapy.
• Fe3O4-carrying vector can be guided to cancer sites under the influence of magnetic fields.
Oral colonic nano-drug delivery system has attracted growing attention in treating colon cancer for their excellent characteristics. However, the unique and complex structure of the gastrointestinal tract is still an obstacle to the safe delivery of drugs targeting sites in colon tumors. Here, we designed magnetically driven dual-targeted oral colonic nanoparticles loaded with chlorogenic acid using pectin and oleic acid-modified iron oxide (Fe3O4@OA). Specific degradation of pectin by pectinase produced by colonic flora and magnetic fields applied to the colon confers specific targeting of nanoparticles to the colon. In order to overcome the challenge of preparing magnetically driven nanoparticles with small and homogeneous particle sizes by a single conventional method, we developed the combined ultrasound-emulsification technique. The average particle size of the prepared nanoparticles was 81.04 ± 1.02 nm, which showed good drug release in the simulated colonic environment. In vitro anticancer studies, the drug-loaded nanoparticles possess an obvious toxicity and apoptosis-inducing ability against cancer cells. Meanwhile, the hemolysis results demonstrated the safety of the nanoplatform (PET/CGA/Fe3O4@OA). This work holds broad prospects as a new treatment modality for colon cancer.