- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
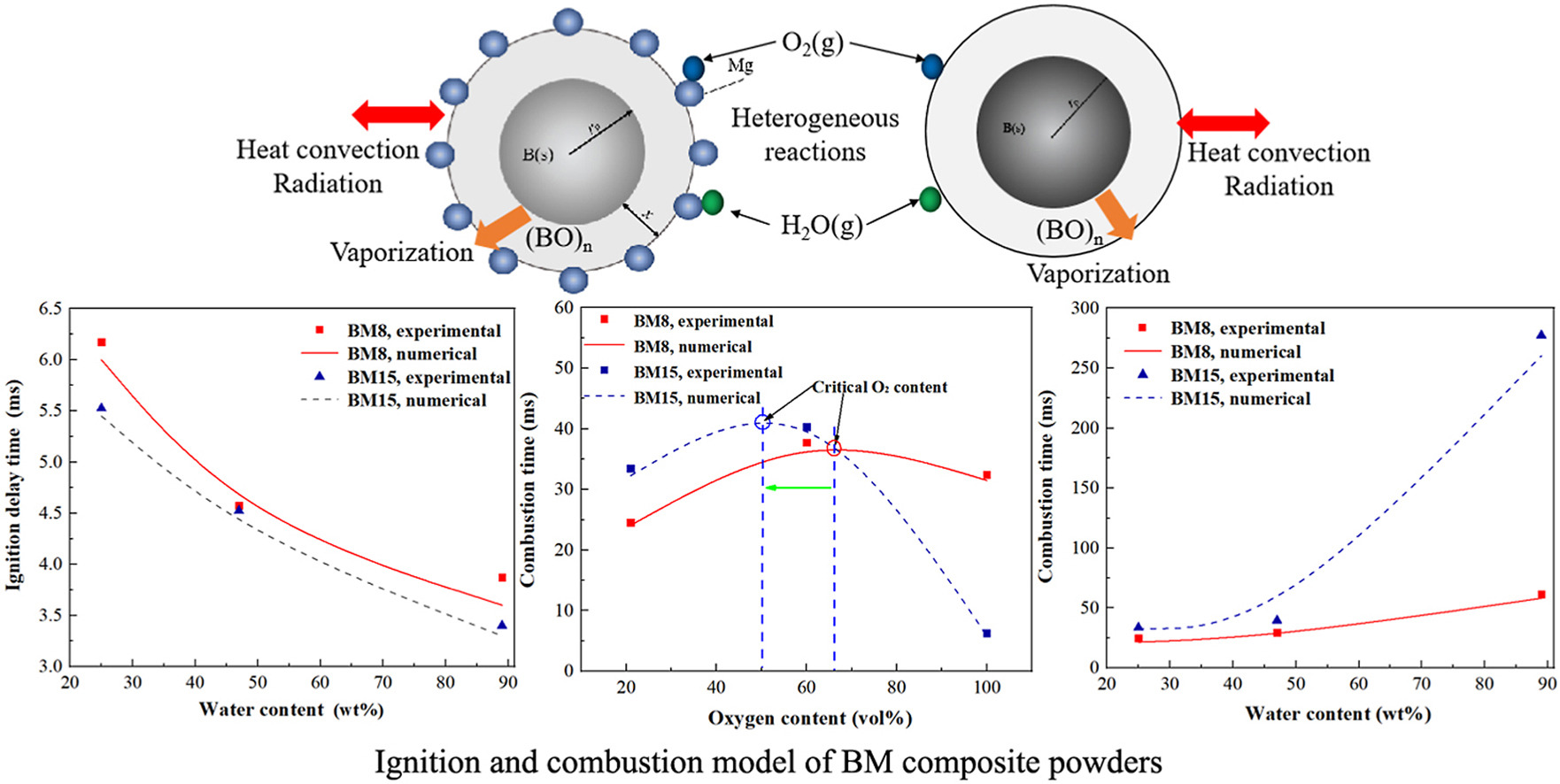
• Developed and validated ignition model for boron-magnesium (BM) powders with Mg inhibiting effect.
• Revealed H2O, O2, Mg content and pressure effects on ignition and combustion time.
• A critical O2 content exists above which combustion time decreases with O2 content.
• There is a trade-off between ignition and combustion performance of BM powders.
A high-pressure laser ignition and combustion system with adjustable oxidizer gas atmosphere is established to investigate the ignition and combustion characteristics of boron-magnesium (BM) composite powders. An ignition and combustion model of BM powders is established and validated in the present study. The results show that increasing water content, O2 content and Mg content all result in shorter ignition delay time of BM powders, among which the effect of water content is the most obvious. However, ignition delay time increases as pressure increases. The combustion time decreases with increasing Mg content and ambient pressure but increases with water content. With the increase of O2 content, combustion time of BM powders first increases and then decreases, which means a critical O2 content exists above which combustion time decreases. The results show that there exists a trade-off between ignition and combustion performance of BM composite powders.