- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
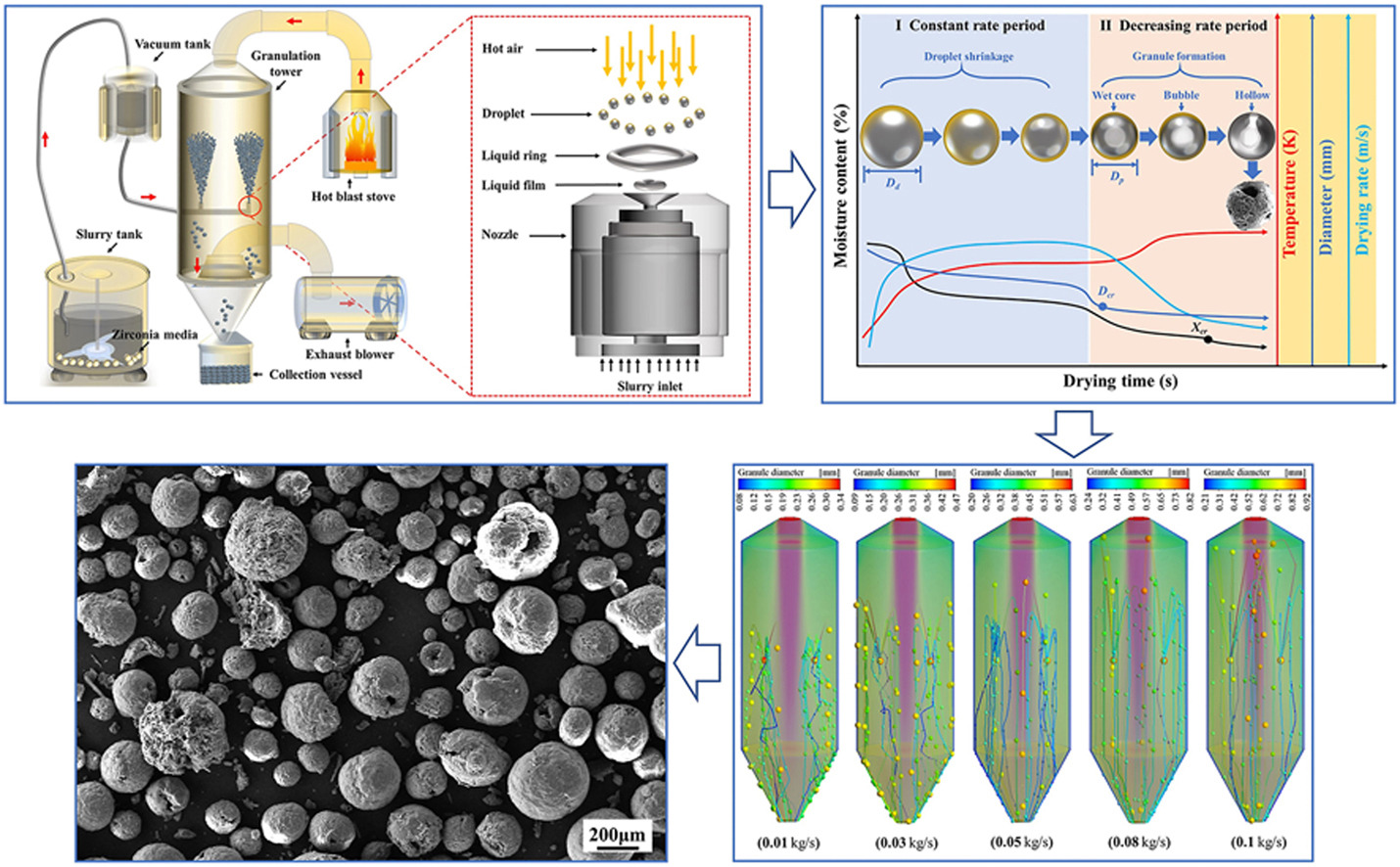
• The formation mechanism of the droplet-to-granule was described.
• The mathematical model of spray drying was constructed.
• A numerical simulation method for spray drying was established.
• The granule's moisture content and diameter distribution were computed.
• The optimum spray drying parameters were determined and applied.
In this work, the formation mechanism of the droplet-to-granule was investigated in detail based on mold powder manufacturing. A specific mathematical model of two-stage spray drying was established to describe droplet and granule motion, heat and mass transfer, and granule morphology during spray drying. Then, the relationships between spray drying parameters (inlet temperature, atomization pressure, slurry mass flow rate) and the properties of the drying tower (temperature and velocity fields) and mold powder granules (temperature, evaporation rates, moisture content, and diameter) were simulated and calculated using ANSYS/Fluent software. To ensure that the granule size of mold powder was controlled within the ideal range (0.2–0.6 mm) for producing granules with appropriate mechanical and metallurgical properties, the following optimum spray drying parameters were chosen based on the results of the numerical simulation: inlet temperatures, 873 K; slurry atomization pressure, 1.8 MPa; slurry mass flow rate, 0.05 kg s−1. Among these parameters, the slurry mass flow rate has the most significant effect on granule size.