- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
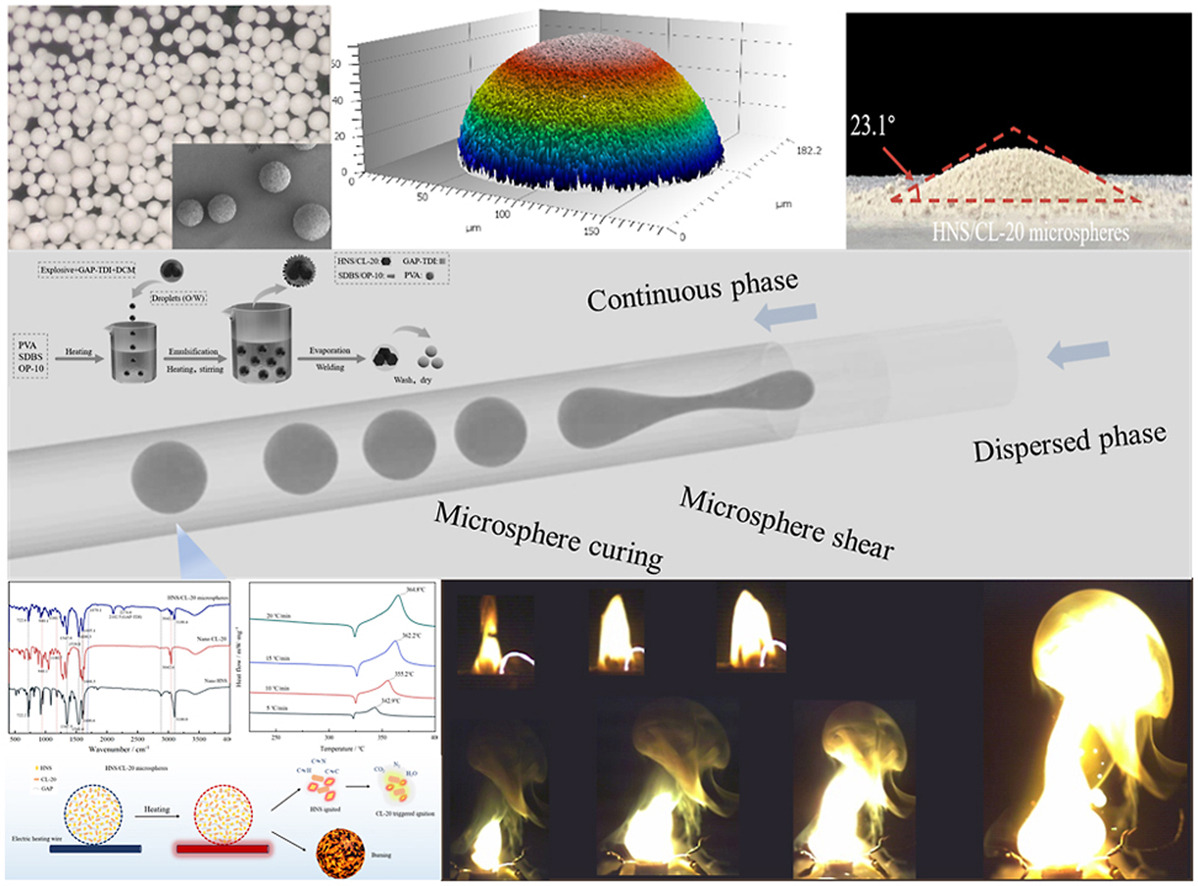
• HNS/CL-20 microspheres were prepared by combining microfluidics and emulsification technology.
• The microspheres retained the crystal structure of CL-20 (ε-type).
• The microspheres have excellent ignition performance and detonation performance.
Improved controllability and energy density of ignition agents are of great significance for the development of energetic composite materials. In this study, droplet microfluidics and emulsification techniques were combined to prepare HNS/CL-20 composite microspheres with polyglycidyl azide polymer (GAP) as the binder. The influence of binder content on the morphology of microspheres was investigated, and the microspheres were characterized and tested for particle size, crystal structure, thermal decomposition, dispersibility, mechanical sensitivity, combustion behavior and detonation performance. The results showed that microspheres prepared with a binder content of 3% had higher sphericity and particle size uniformity. The microspheres retained the crystal structure of both HNS and CL-20 (ε-type). Compared with raw HNS, the microspheres had higher apparent activation energy, better safety performance, and good dispersibility. The ignition experiments and detonation performance tests show that HNS/CL-20 composite microspheres have excellent ignition performance, obvious combustion flame, and significant energy release effects, which are expected to achieve high energy and high-speed response of the igniter, thus improving the ignition reliability in special environments or systems.