- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
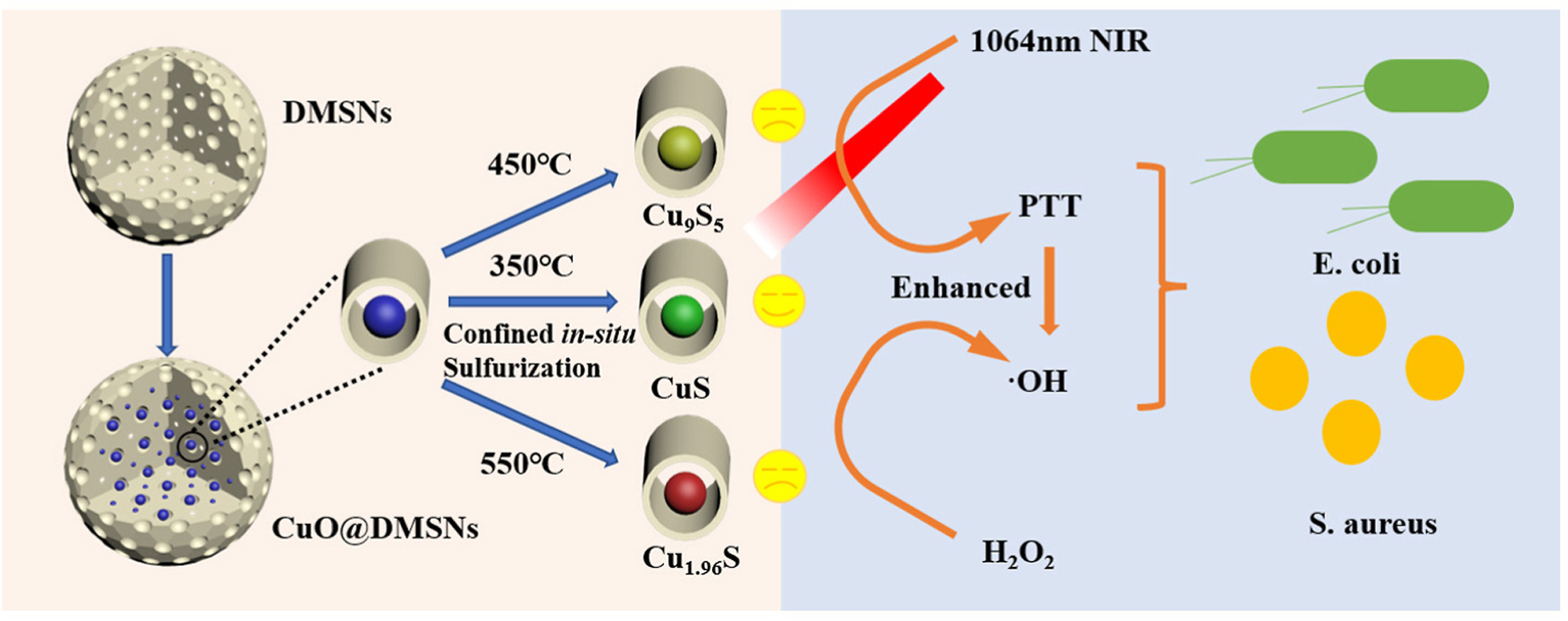
• CuxSy@DMSNs is prepared by a confined in situ sulfurization method.
• Crystal phase of CuxSy can be controlled by changing sulfurization temperature.
• CuS@DMSNs have high NIR-Ⅱ photothermal conversion efficiency of 36.86%.
• Peroxidase-like activity of CuS@DMSNs can be enhanced by photothermal exposure.
• CuS@p-DMSNs shows good antibacterial properties with 1064 nm NIR and H2O2.
Bacteria-caused wound infection greatly threatens human health, thus developing an efficient and safe antibacterial agent without drug resistance is still a great challenge. Herein, a confined vulcanization strategy is proposed to construct copper sulfides-loaded dual-mesoporous silica nanospheres (CuxSy@DMSNs) with various crystal phases for reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated and photothermal antibacterial application. With the pore confinement of DMSNs, the crystal phases of copper sulfides including CuS, Cu9S5 and Cu1.96S can be easily controlled by changing the vulcanization temperature. The relationships between the crystal phases and photothermal properties as well as peroxidase-like activity of copper sulfides were systematically investigated. Results show that the obtained CuS@DMSNs exhibited higher photothermal ability with remarkable photothermal conversion efficiency of 36.86% in the second near-infrared region (NIR-II) and better peroxidase-like activity, compared to those of Cu9S5@DMSNs and Cu1.96S@DMSNs. As a result, the in vitro experiments showed the good antibacterial effect against both gram-negative E. coli and gram-positive S. aureus under 1064 nm laser irradiation and the presence of H2O2. Besides, the CCK-8 assay indicated that CuS@p-DMSNs have minimal cytotoxicity against normal human umbilical vein endothelial cells at the ranged concentrations. Therefore, the resultant CuS@p-DMSNs could act as a promising antibacterial agent for deep wound bacterial infection treatment.