- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
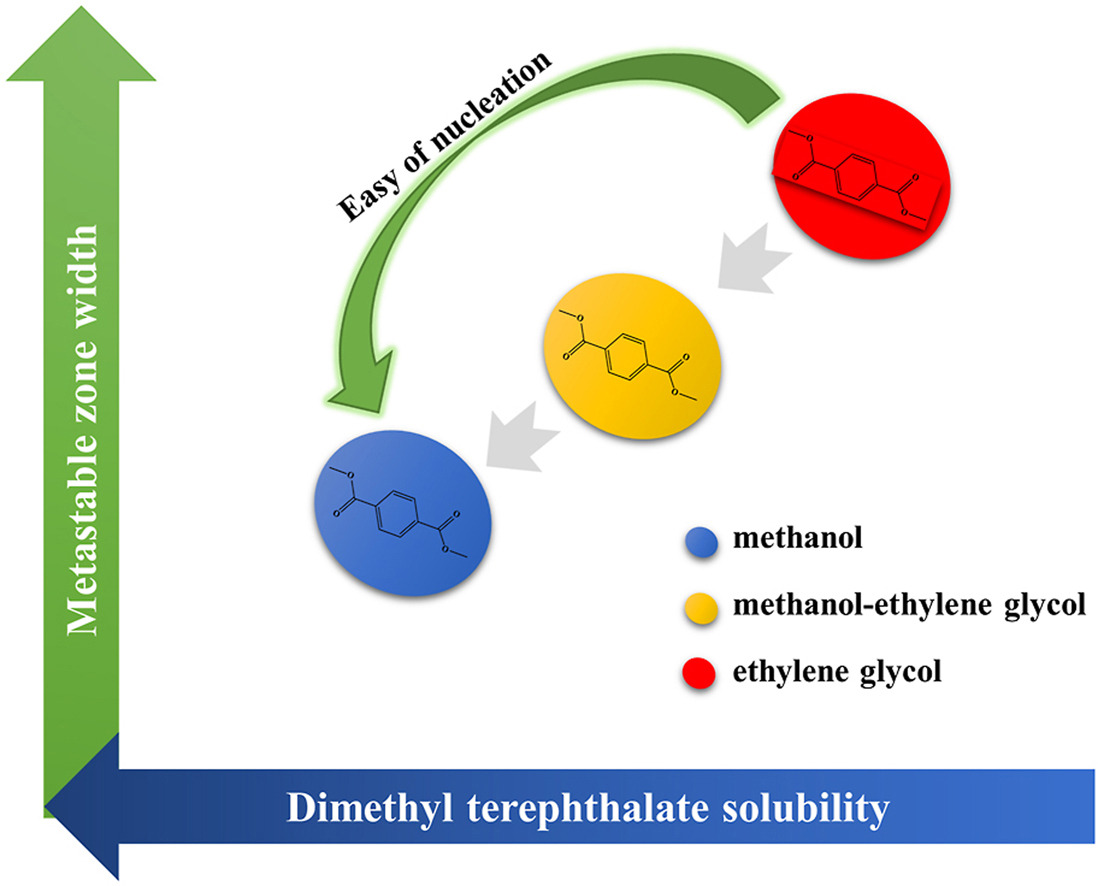
• Correlation of solubility data using seven different solubility models.
• Exploration of metastable zone width and solubility variation in mixed solvent system.
• Effects of saturation temperature and solvent system on nucleation kinetics were investigated.
• Correlation between nucleation drive and solid-liquid interface energy was discussed.
Dissolution and nucleation are two essential processes for industrial crystallization. This paper investigates the effect of ethylene glycol addition on the crystallization behavior of dimethyl terephthalate (DMT) in solution. The DMT solubility in mixed solvent system (methanol-ethylene glycol) was determined by isothermal satiation approach, and the solubility was associated using seven models. The model fitting results were consistent with the experimental values. Based on the results, the metastable zone width (MSZW) of DMT was detected by the polythermal approach; the modified Sangwal's theory was used to investigate the nucleation behavior, which can provide a new way of thought for better analysis of the crystallization behavior. The results demonstrated that MSZW was associated with various elements, such as cooling rate, saturation temperature and mass fraction of ethylene glycol. The addition of ethylene glycol slowed down the nucleation rate as shown by the broadening of MSZW. We derive the solid-liquid interface energy, the nucleation driving force, the critical nucleation size and the critical Gibbs free energy according to the classical nucleation theory. It is demonstrated that the nucleation driving force and the solid-liquid interface energy are dependent and jointly influence the MSZW.