- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
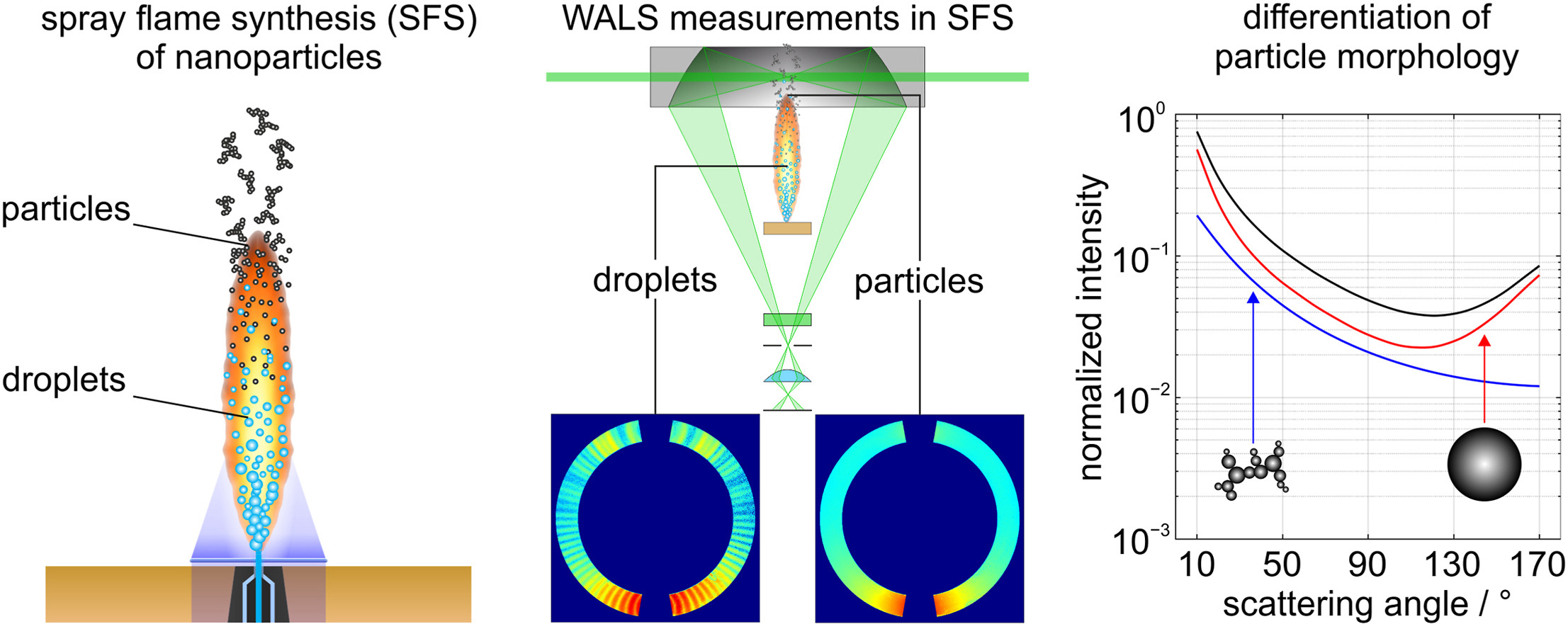
• In situ characterization of spray flame synthesis using wide-angle light scattering.
• Distinction between scattering of droplets and nanoparticles of different morphology.
• Observation of different morphologies for titania and iron oxide nanoparticles.
Wide-angle light scattering (WALS) was used for in situ measurements of droplet and nanoparticle size distributions during the synthesis of titania and iron oxide particles from liquid precursor solutions in the standardized SpraySyn burner for spray flame synthesis. Titania was synthesized from titanium tetraisopropoxide (TTIP) and iron oxide from iron(III) nitrate nonahydrate (INN) using ethanol (EtOH) as solvent. Scattering images were taken at heights up to 120 mm above the burner surface and classified into droplet and particle scattering. Droplet size distributions were derived from a sequential analysis of scattering data containing the oscillating Mie pattern, the lognormal size distribution parameters for spherical and fractal particle fractions from a multivariate approach on averaged particle scattering data. The results show that the precursor addition leads to altered evaporation behavior and even droplet disruption probably induced by puffing or micro-explosions compared to pure EtOH. In the case of TTIP (a hygroscopic alkoxide), the synthesis of a large fraction of spheres was observed, while the nitrate INN leads to the formation of mostly fractal aggregates.