- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
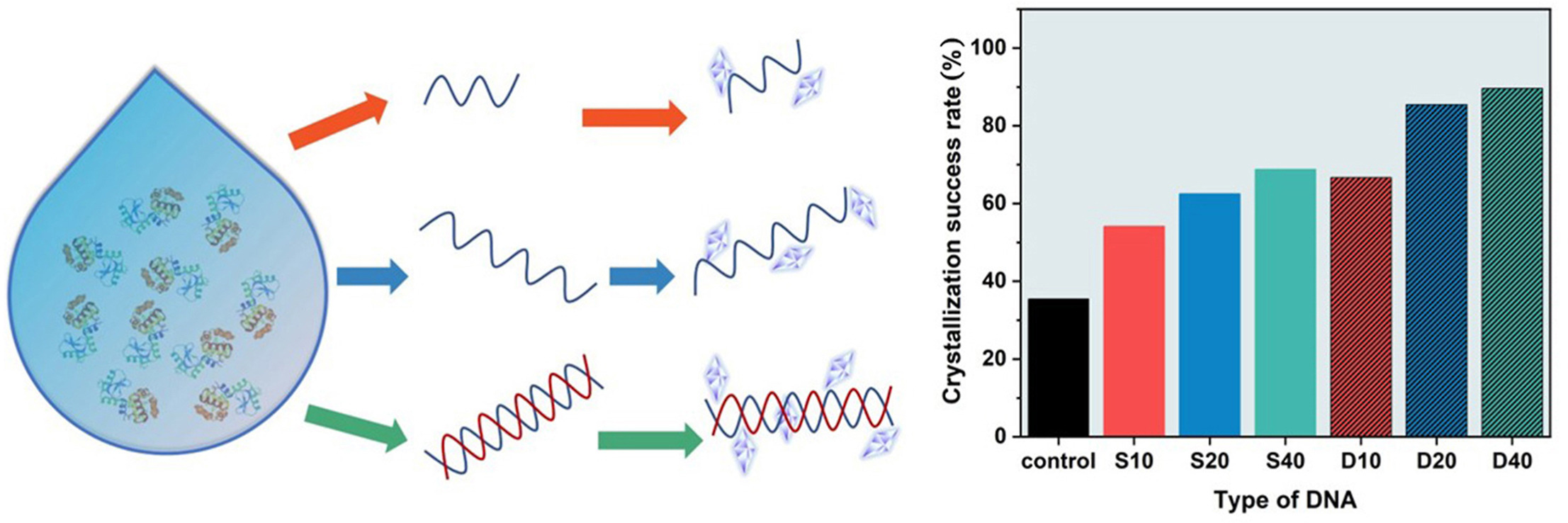
• DNA polymeric additive templates effectively promotes protein crystallization efficiency.
• DNA promotes protein crystallization success rate, crystal number and mean size, crystallization rate and time.
• Better promotion of DNA templates when protein concentration is low.
• Facilitation: double-stranded DNA > single-stranded DNA, long-stranded DNA > short-stranded DNA.
Protein crystallization plays a significant role in three-dimensional structural analysis and protein purification. It is important to increase the crystallization efficiency, which is possible by adding heterogeneous templates in crystallization systems. DNA is biologically compatible and artificially designable polymer, which is easy to extract. In this study, single- and double-stranded DNA of precise sequences were designed and used as templates to promote protein crystallization of lysozyme and catalase. Influence of DNA, single-stranded DNA with 10, 20, 40 bases and double-stranded DNA with 10, 20, 40 base pairs, were investigated. The success rate of obtaining crystals of lysozyme and catalase in equal period was significantly improved with the addition of DNA comparing without templates added. Double-stranded DNA led to higher nucleation rate than that with single-stranded DNA. The promotion of nucleation was more obvious at low concentration of protein solution and with longer chain DNA templates. Crystal number and crystallization rate was enhanced with addition of long double-stranded DNA templates. All the results confirm that DNA is an effective polymer additive to enhance protein crystallization, especially for the application of the scarce protein crystallization.